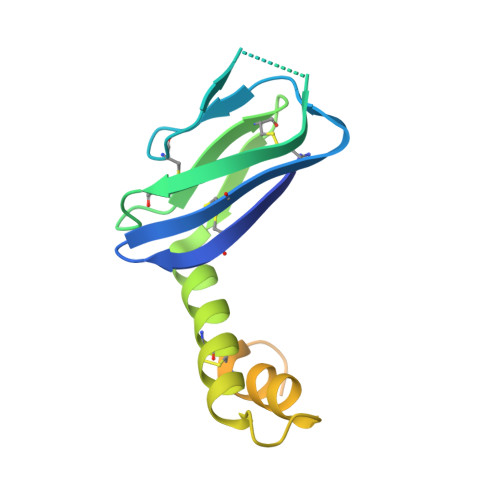
The Hantavirus Surface Glycoprotein Lattice and Its Fusion Control Mechanism.
Serris, A., Stass, R., Bignon, E.A., Muena, N.A., Manuguerra, J.C., Jangra, R.K., Li, S., Chandran, K., Tischler, N.D., Huiskonen, J.T., Rey, F.A., Guardado-Calvo, P.(2020) Cell 183: 442
- PubMed: 32937107
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.023
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6Y5F, 6Y5W, 6Y62, 6Y68, 6Y6P, 6Y6Q, 6YRB, 6YRQ, 6ZJM - PubMed Abstract:
Hantaviruses are rodent-borne viruses causing serious zoonotic outbreaks worldwide for which no treatment is available. Hantavirus particles are pleomorphic and display a characteristic square surface lattice. The envelope glycoproteins Gn and Gc form heterodimers that further assemble into tetrameric spikes, the lattice building blocks. The glycoproteins, which are the sole targets of neutralizing antibodies, drive virus entry via receptor-mediated endocytosis and endosomal membrane fusion. Here we describe the high-resolution X-ray structures of the heterodimer of Gc and the Gn head and of the homotetrameric Gn base. Docking them into an 11.4-Å-resolution cryoelectron tomography map of the hantavirus surface accounted for the complete extramembrane portion of the viral glycoprotein shell and allowed a detailed description of the surface organization of these pleomorphic virions. Our results, which further revealed a built-in mechanism controlling Gc membrane insertion for fusion, pave the way for immunogen design to protect against pathogenic hantaviruses.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut Pasteur, Structural Virology Unit, and CNRS UMR 3569, Paris, France.