Molecular basis of sidekick-mediated cell-cell adhesion and specificity.
Goodman, K.M., Yamagata, M., Jin, X., Mannepalli, S., Katsamba, P.S., Ahlsen, G., Sergeeva, A.P., Honig, B., Sanes, J.R., Shapiro, L.(2016) Elife 5
- PubMed: 27644106
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.19058
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5K6U, 5K6V, 5K6W, 5K6X, 5K6Y, 5K6Z, 5K70 - PubMed Abstract:
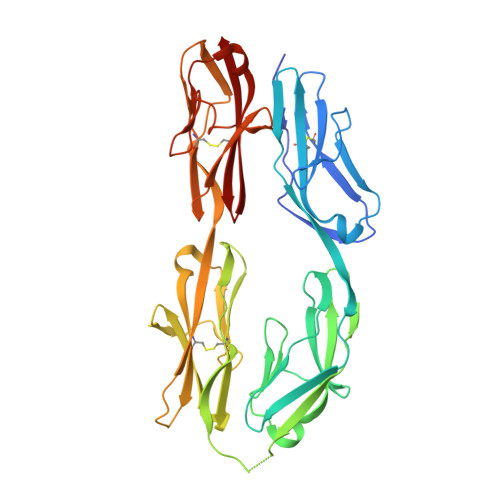
Sidekick (Sdk) 1 and 2 are related immunoglobulin superfamily cell adhesion proteins required for appropriate synaptic connections between specific subtypes of retinal neurons. Sdks mediate cell-cell adhesion with homophilic specificity that underlies their neuronal targeting function. Here we report crystal structures of Sdk1 and Sdk2 ectodomain regions, revealing similar homodimers mediated by the four N-terminal immunoglobulin domains (Ig1-4), arranged in a horseshoe conformation. These Ig1-4 horseshoes interact in a novel back-to-back orientation in both homodimers through Ig1:Ig2, Ig1:Ig1 and Ig3:Ig4 interactions. Structure-guided mutagenesis results show that this canonical dimer is required for both Sdk-mediated cell aggregation (via trans interactions) and Sdk clustering in isolated cells (via cis interactions). Sdk1/Sdk2 recognition specificity is encoded across Ig1-4, with Ig1-2 conferring the majority of binding affinity and differential specificity. We suggest that competition between cis and trans interactions provides a novel mechanism to sharpen the specificity of cell-cell interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, Columbia University, New York, United States.