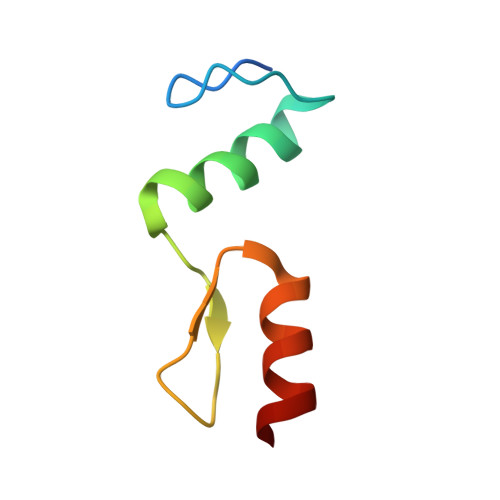
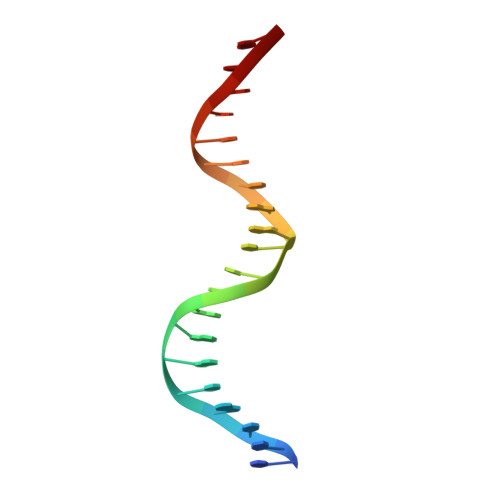
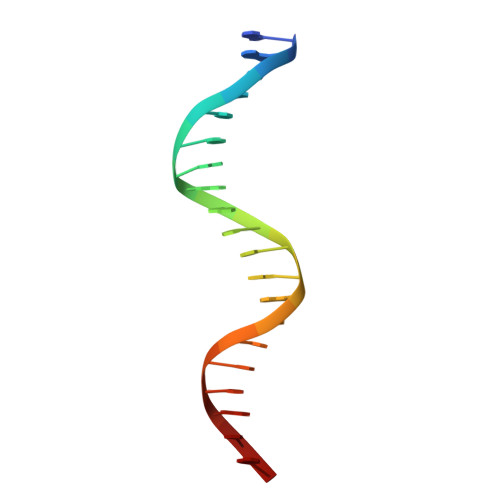
New insights into DNA recognition by zinc fingers revealed by structural analysis of the oncoprotein ZNF217.
Vandevenne, M., Jacques, D.A., Artuz, C., Nguyen, C.D., Kwan, A.H., Segal, D.J., Matthews, J.M., Crossley, M., Guss, J.M., Mackay, J.P.(2013) J Biol Chem 288: 10616-10627
- PubMed: 23436653
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.441451
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4F2J, 4IS1 - PubMed Abstract:
Classical zinc fingers (ZFs) are one of the most abundant and best characterized DNA-binding domains. Typically, tandem arrays of three or more ZFs bind DNA target sequences with high affinity and specificity, and the mode of DNA recognition is sufficiently well understood that tailor-made ZF-based DNA-binding proteins can be engineered. We have shown previously that a two-zinc finger unit found in the transcriptional coregulator ZNF217 recognizes DNA but with an affinity and specificity that is lower than other ZF arrays. To investigate the basis for these differences, we determined the structure of a ZNF217-DNA complex. We show that although the overall position of the ZFs on the DNA closely resembles that observed for other ZFs, the side-chain interaction pattern differs substantially from the canonical model. The structure also reveals the presence of two methyl-π interactions, each featuring a tyrosine contacting a thymine methyl group. To our knowledge, interactions of this type have not previously been described in classical ZF-DNA complexes. Finally, we investigated the sequence specificity of this two-ZF unit and discuss how ZNF217 might discriminate its target DNA sites in the cell.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Molecular Bioscience, University of Sydney, New South Wales, 2006 Australia.