Novel Scorpion Toxin omega-Buthitoxin-Hf1a Selectively Inhibits Calcium Influx via Ca V 3.3 and Ca V 3.2 and Alleviates Allodynia in a Mouse Model of Acute Postsurgical Pain.
Wang, D., Herzig, V., Dekan, Z., Rosengren, K.J., Payne, C.D., Hasan, M.M., Zhuang, J., Bourinet, E., Ragnarsson, L., Alewood, P.F., Lewis, R.J.(2024) Int J Mol Sci 25
- PubMed: 38731963
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094745
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9BFL - PubMed Abstract:
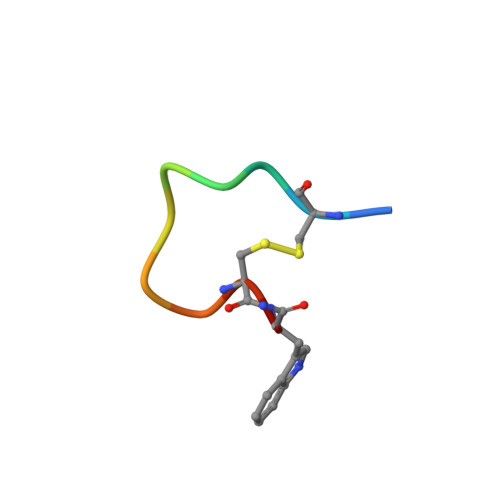
Venom peptides have evolved to target a wide range of membrane proteins through diverse mechanisms of action and structures, providing promising therapeutic leads for diseases, including pain, epilepsy, and cancer, as well as unique probes of ion channel structure-function. In this work, a high-throughput FLIPR window current screening assay on T-type Ca V 3.2 guided the isolation of a novel peptide named ω-Buthitoxin-Hf1a from scorpion Hottentotta franzwerneri crude venom. At only 10 amino acid residues with one disulfide bond, it is not only the smallest venom peptide known to target T-type Ca V s but also the smallest structured scorpion venom peptide yet discovered. Synthetic Hf1a peptides were prepared with C-terminal amidation (Hf1a-NH 2 ) or a free C-terminus (Hf1a-OH). Electrophysiological characterization revealed Hf1a-NH 2 to be a concentration-dependent partial inhibitor of Ca V 3.2 (IC 50 = 1.18 μM) and Ca V 3.3 (IC 50 = 0.49 μM) depolarized currents but was ineffective at Ca V 3.1. Hf1a-OH did not show activity against any of the three T-type subtypes. Additionally, neither form showed activity against N-type Ca V 2.2 or L-type calcium channels. The three-dimensional structure of Hf1a-NH 2 was determined using NMR spectroscopy and used in docking studies to predict its binding site at Ca V 3.2 and Ca V 3.3. As both Ca V 3.2 and Ca V 3.3 have been implicated in peripheral pain signaling, the analgesic potential of Hf1a-NH 2 was explored in vivo in a mouse model of incision-induced acute post-surgical pain. Consistent with this role, Hf1a-NH 2 produced antiallodynia in both mechanical and thermal pain.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, School of Pharmacy, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China.