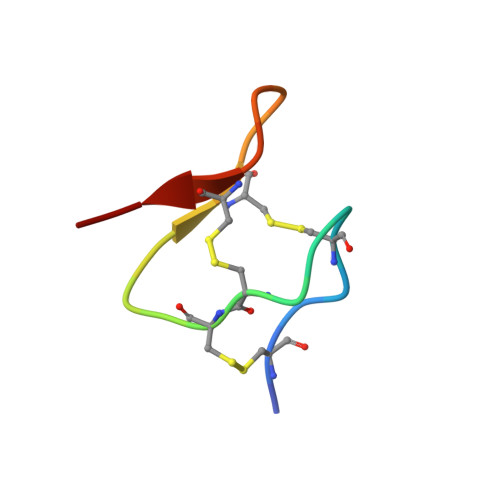
Structural analysis of a U-superfamily conotoxin containing a mini-granulin fold: Insights into key features that distinguish between the ICK and granulin folds.
Raffaelli, T., Wilson, D.T., Dutertre, S., Giribaldi, J., Vetter, I., Robinson, S.D., Thapa, A., Widi, A., Loukas, A., Daly, N.L.(2024) J Biol Chem 300: 107203-107203
- PubMed: 38508311
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107203
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8UXR - PubMed Abstract:
We are entering an exciting time in structural biology where artificial intelligence can be used to predict protein structures with greater accuracy than ever before. Extending this level of accuracy to the predictions of disulfide-rich peptide structures is likely to be more challenging, at least in the short term, given the tight packing of cysteine residues and the numerous ways that the disulfide bonds can potentially be linked. It has been previously shown in many cases that several disulfide bond connectivities can be accommodated by a single set of NMR-derived structural data without significant violations. Disulfide-rich peptides are prevalent throughout nature, and arguably the most well-known are those present in venoms from organisms such as cone snails. Here, we have determined the first three-dimensional structure and disulfide connectivity of a U-superfamily cone snail venom peptide, TxVIIB. TxVIIB has a VI/VII cysteine framework that is generally associated with an inhibitor cystine knot (ICK) fold; however, AlphaFold predicted that the peptide adopts a mini-granulin fold with a granulin disulfide connectivity. Our experimental studies using NMR spectroscopy and orthogonal protection of cysteine residues indicate that TxVIIB indeed adopts a mini-granulin fold but with the ICK disulfide connectivity. Our findings provide structural insight into the underlying features that govern formation of the mini-granulin fold rather than the ICK fold and will provide fundamental information for prediction algorithms, as the subtle complexity of disulfide isomers may be not adequately addressed by the current prediction algorithms.
Organizational Affiliation:
Australian Institute of Tropical Health and Medicine, James Cook University, Cairns, Australia.