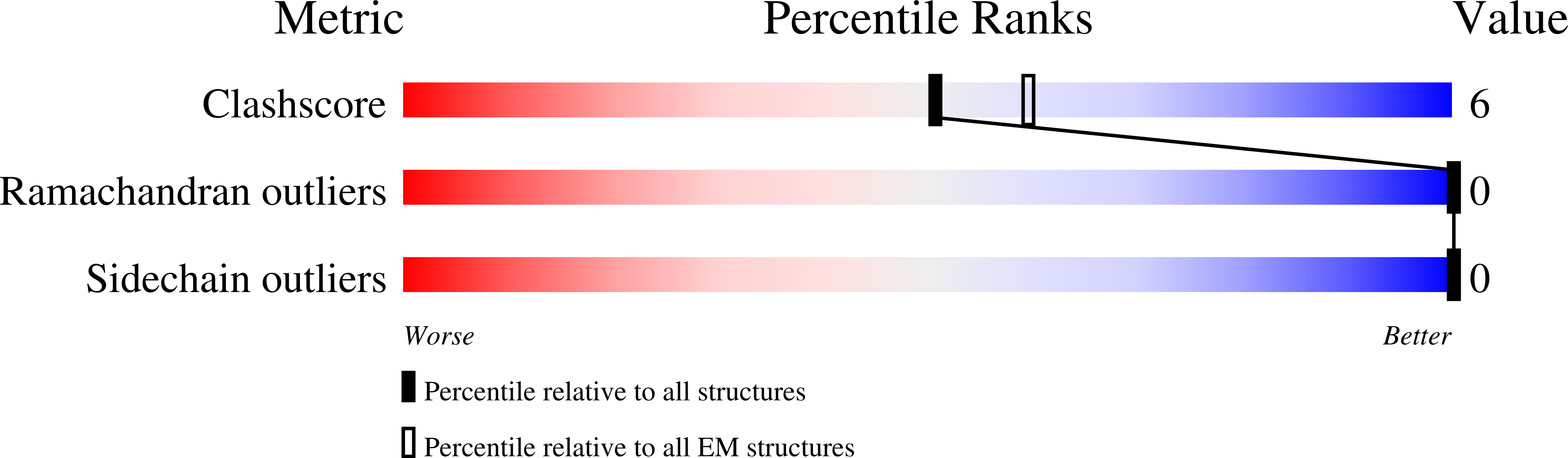Inside and outside of virus-like particles HBc and HBc/4M2e: A comprehensive study of the structure.
Egorov, V.V., Shvetsov, A.V., Pichkur, E.B., Shaldzhyan, A.A., Zabrodskaya, Y.A., Vinogradova, D.S., Nekrasov, P.A., Gorshkov, A.N., Garmay, Y.P., Kovaleva, A.A., Stepanova, L.A., Tsybalova, L.M., Shtam, T.A., Myasnikov, A.G., Konevega, A.L.(2022) Biophys Chem 293: 106943-106943
- PubMed: 36495688
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpc.2022.106943
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8BDZ, 8BER - PubMed Abstract:
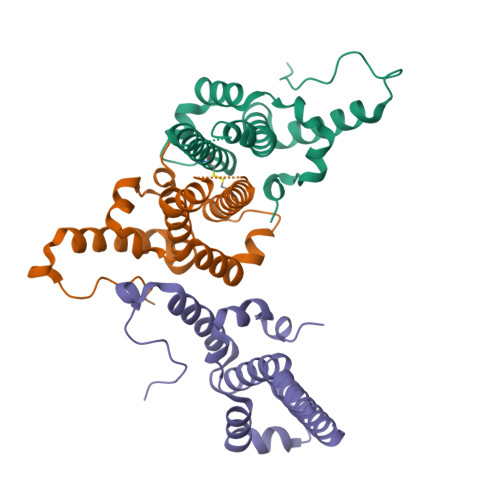
Hepatitis B virus core antigen (HBc) with the insertion of four external domains of the influenza A M2 protein (HBc/4M2e) form virus-like particles whose structure was studied using a combination of molecular modeling and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). It was also shown that self-assembling of the particles occurs inside bacterial cells, but despite the big inner volume of the core shell particle, purified HBc/4M2e contain an insignificant amount of bacterial proteins. It was shown that a fragment of the M2e corresponding to 4M2e insertion is prone to formation of amyloid-like fibrils. However, as the part of the immunodominant loop, M2e insertion does not show a tendency to intermolecular interaction. A full-atomic HBc-4M2e model with the resolution of about 3 Å (3.13 Å for particles of Т = 4 symmetry, 3.7 Å for particles of Т = 3 symmetry) was obtained by molecular modeling methods based on cryo-EM data.
Organizational Affiliation:
Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute named by B.P. Konstantinov of National Research Centre «Kurchatov Institute», Orlova roscha 1, Gatchina 188300, Russian Federation; Smorodintsev Research Institute of Influenza, Russian Ministry of Health, 197376, Prof. Popov St. 15/17, St. Petersburg, Russian Federation; National Research Center "Kurchatov Institute", Akademika Kurchatova pl. 1, 123182 Moscow, Russian Federation; Institute of Experimental Medicine, Academika Pavlova, 12, 197376 St. Petersburg, Russian Federation. Electronic address: sondyn@yandex.ru.