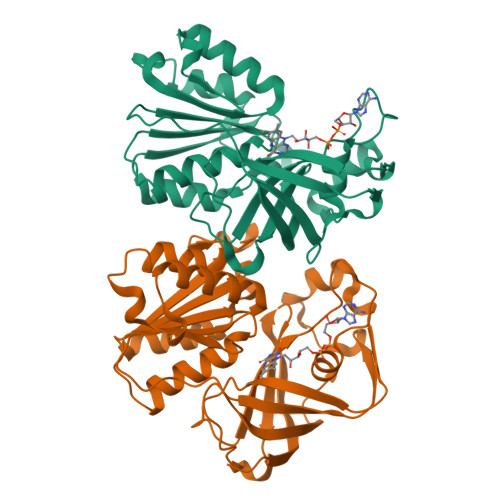
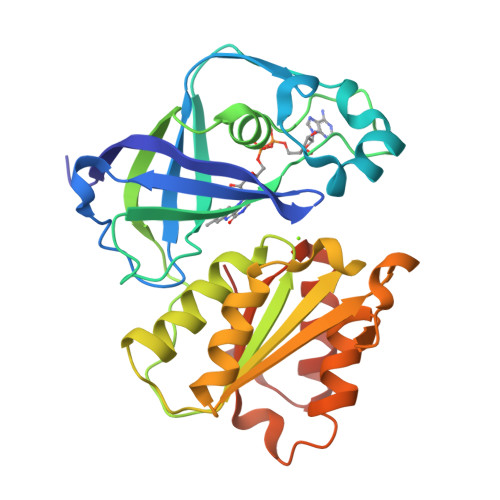
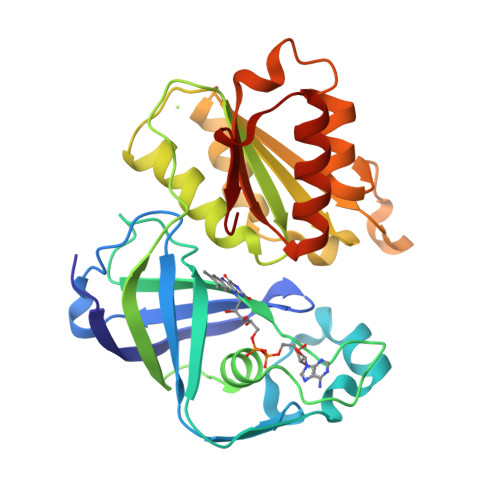
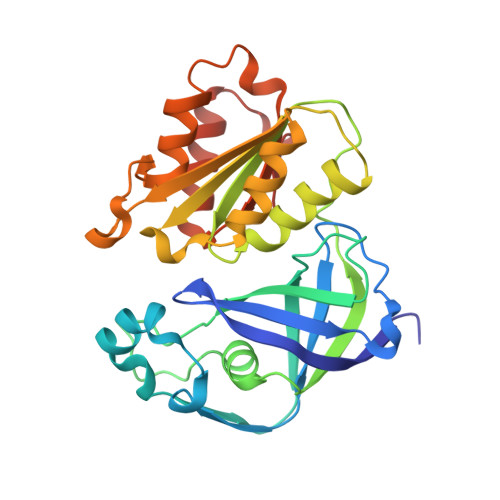
Conformational coupling of redox-driven Na + -translocation in Vibrio cholerae NADH:quinone oxidoreductase.
Hau, J.L., Kaltwasser, S., Muras, V., Casutt, M.S., Vohl, G., Claussen, B., Steffen, W., Leitner, A., Bill, E., Cutsail 3rd, G.E., DeBeer, S., Vonck, J., Steuber, J., Fritz, G.(2023) Nat Struct Mol Biol 30: 1686-1694
- PubMed: 37710014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-023-01099-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8A1T, 8A1U, 8A1V, 8A1W, 8A1X, 8A1Y, 8ACW, 8ACY, 8AD3, 8AD4, 8AD5 - PubMed Abstract:
In the respiratory chain, NADH oxidation is coupled to ion translocation across the membrane to build up an electrochemical gradient. In the human pathogen Vibrio cholerae, the sodium-pumping NADH:quinone oxidoreductase (Na + -NQR) generates a sodium gradient by a so far unknown mechanism. Here we show that ion pumping in Na + -NQR is driven by large conformational changes coupling electron transfer to ion translocation. We have determined a series of cryo-EM and X-ray structures of the Na + -NQR that represent snapshots of the catalytic cycle. The six subunits NqrA, B, C, D, E, and F of Na + -NQR harbor a unique set of cofactors that shuttle the electrons from NADH twice across the membrane to quinone. The redox state of a unique intramembranous [2Fe-2S] cluster orchestrates the movements of subunit NqrC, which acts as an electron transfer switch. We propose that this switching movement controls the release of Na + from a binding site localized in subunit NqrB.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Cellular Microbiology, Institute of Biology, University of Hohenheim, Stuttgart, Germany.