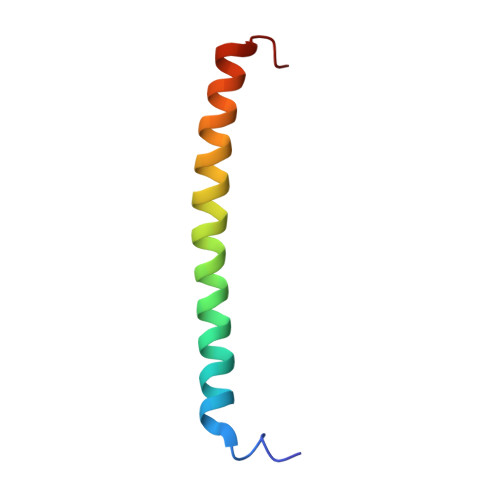
NMR solution structure of the N-terminal domain of subunit E (E1-52) of A1AO ATP synthase from Methanocaldococcus jannaschii
Gayen, S., Balakrishna, A.M., Gruber, G.(2009) J Bioenerg Biomembr 41: 343-348
- PubMed: 19760172
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-009-9237-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2KK7 - PubMed Abstract:
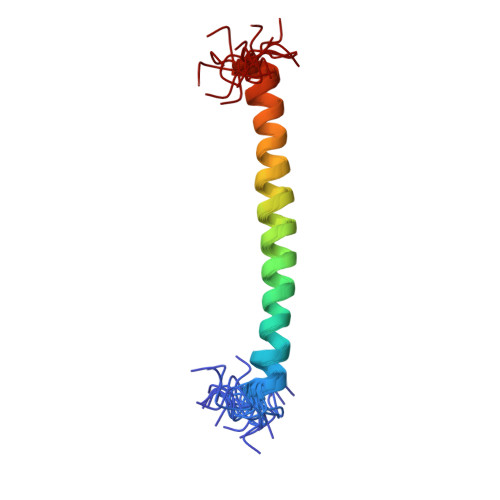
The N-termini of E and H of A1AO ATP synthase have been shown to interact and an NMR structure of N-terminal H1-47 has been solved recently. In order to understand the E-H assembly and the N-terminal structure of E, the truncated construct E1-52 of Methanocaldococcus jannaschii A1AO ATP synthase was produced, purified and the solution structure of E1-52 was determined by NMR spectroscopy. The protein is 60.5 A in length and forms an alpha helix between the residues 8-48. The molecule is amphipathic with a strip of hydrophobic residues, discussed as a possible helix-helix interaction with neighboring subunit H.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biological Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, 60 Nanyang Drive, Nanyang 637551, Singapore.