Structural basis of G-tract recognition and encaging by hnRNP F quasi-RRMs.
Dominguez, C., Fisette, J.F., Chabot, B., Allain, F.H.(2010) Nat Struct Mol Biol 17: 853-861
- PubMed: 20526337
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1814
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
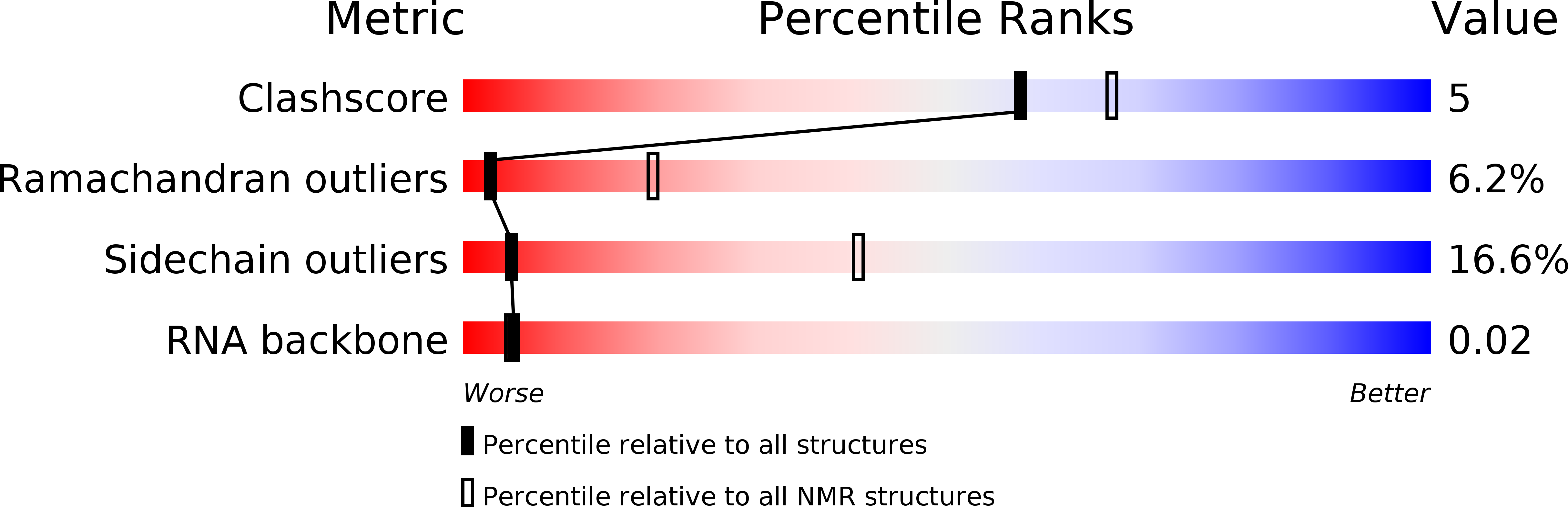
2KFY, 2KG0, 2KG1 - PubMed Abstract:
The heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) F is involved in the regulation of mRNA metabolism by specifically recognizing G-tract RNA sequences. We have determined the solution structures of the three quasi-RNA-recognition motifs (qRRMs) of hnRNP F in complex with G-tract RNA. These structures show that qRRMs bind RNA in a very unusual manner, with the G-tract 'encaged', making the qRRM a novel RNA binding domain. We defined a consensus signature sequence for qRRMs and identified other human qRRM-containing proteins that also specifically recognize G-tract RNAs. Our structures explain how qRRMs can sequester G-tracts, maintaining them in a single-stranded conformation. We also show that isolated qRRMs of hnRNP F are sufficient to regulate the alternative splicing of the Bcl-x pre-mRNA, suggesting that hnRNP F would act by remodeling RNA secondary and tertiary structures.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biophysics, ETH Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland.