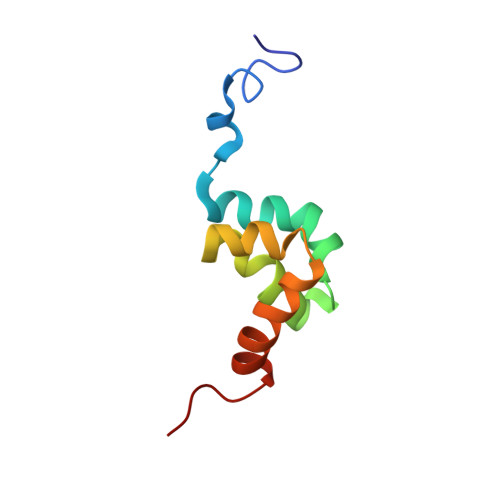
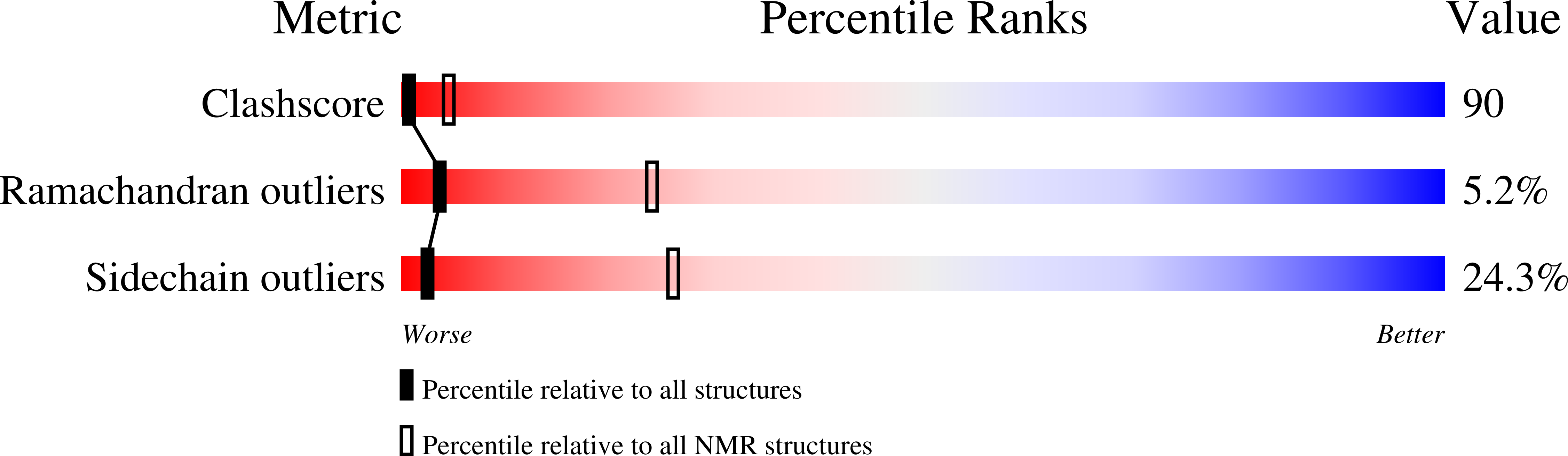Solution structure of the PABC domain from wheat poly (A)-binding protein: an insight into RNA metabolic and translational control in plants
Siddiqui, N., Osborne, M.J., Gallie, D.R., Gehring, K.(2007) Biochemistry 46: 4221-4231
- PubMed: 17358048
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi061986d
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2DYD - PubMed Abstract:
In animals, the PABC domain from poly (A)-binding protein recruits proteins containing a specific interacting motif (PAM-2) to the mRNP complex. These proteins include Paip1, Paip2, and eukaryotic release factor 3 (eRF3), all of which regulate PABP function in translation. The following reports the solution structure of PABC from Triticum avestium (wheat) poly (A)-binding protein determined by NMR spectroscopy. Wheat PABC (wPABC) is an alpha-helical protein domain, which displays a fold highly similar to the human PABC domain and contains a PAM-2 peptide binding site. Through a bioinformatics search, several plant proteins containing a PAM-2 site were identified including the early response to dehydration protein (ERD-15), which was previously shown to regulate PABP-dependent translation. The plant PAM-2 proteins contain a variety of conserved sequences including a PABP-interacting 1 motif (PAM-1), RNA binding domains, an SMR endonuclease domain, and a poly (A)-nuclease regulatory domain, all of which suggest a function in either translation or mRNA metabolism. The proteins identified are well conserved throughout plant species but have no sequence homologues in metazoans. We show that wPABC binds to the plant PAM-2 motif with high affinity through a conserved mechanism. Overall, our results suggest that plant species have evolved a distinct regulatory mechanism involving novel PABP binding partners.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, McGill University, 3655 Promenade Sir William Osler, QC H3G-1Y6, Canada.