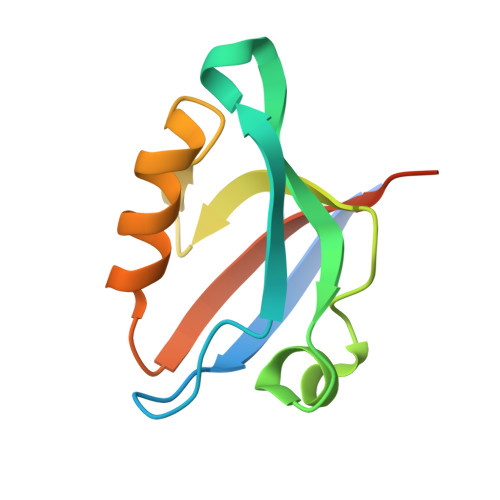
Solution structure of GOPC PDZ domain and its interaction with the C-terminal motif of neuroligin
Li, X., Zhang, J., Cao, Z., Wu, J., Shi, Y.(2006) Protein Sci 15: 2149-2158
- PubMed: 16882988
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.062087506
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2DC2 - PubMed Abstract:
GOPC (Golgi-associated PDZ and coiled-coil motif-containing protein) represents a PDZ domain-containing protein associated with the Golgi apparatus, which plays important roles in vesicular trafficking in secretory and endocytic pathways. GOPC interacts with many other proteins, such as the Wnt receptors Frizzled 8 and neuroligin via its PDZ domain. Neuroligin is a neural cell-adhesion molecule of the post-synapse, which binds to the presynapse molecule neurexin to form a heterotypic intercellular junction. Here we report the solution structure of the GOPC PDZ domain by NMR. Our results show that it is a canonical class I PDZ domain, which contains two alpha-helices and six beta-strands. Using chemical shift perturbation experiments, we further studied the binding properties of the GOPC PDZ domain with the C-terminal motif of neuroligin. The observations showed that the ensemble of the interaction belongs to fast exchange with low affinity. The 3D model of the GOPC PDZ domain/neuroligin C-terminal peptide complex was constructed with the aid of the molecular dynamics simulation method. Our discoveries provide insight into the specific interaction of the GOPC PDZ domain with the C-terminal peptide of Nlg and also provide a general insight about the possible binding mode of the interaction of Nlg with other PDZ domain-containing proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at Microscale, People's Republic of China.