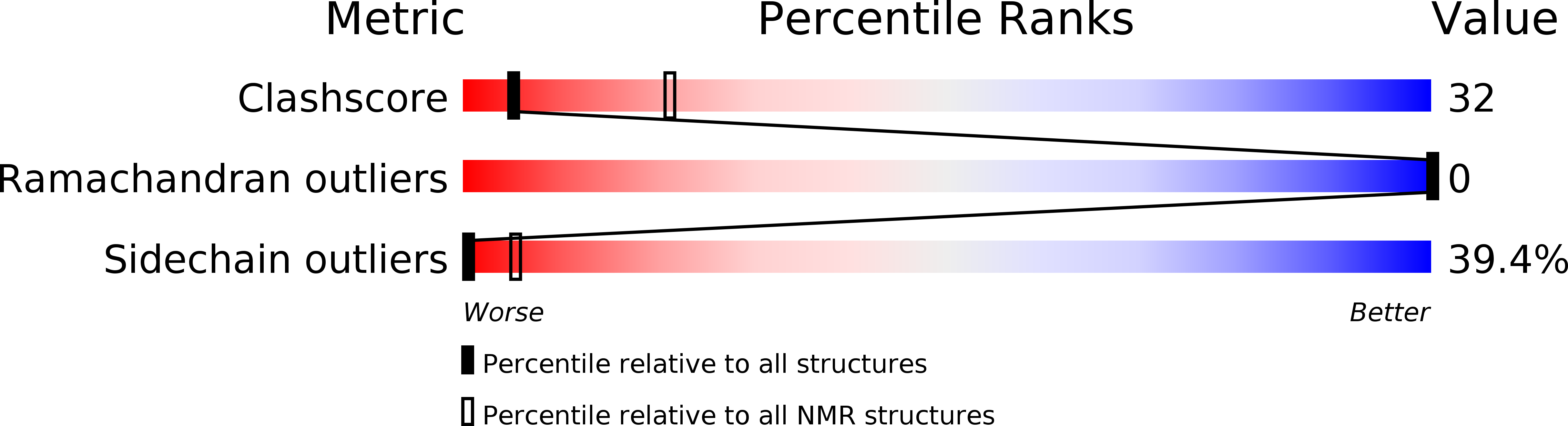Solution structure of a C-terminal coiled-coil domain from bovine IF(1): the inhibitor protein of F(1) ATPase.
Gordon-Smith, D.J., Carbajo, R.J., Yang, J.C., Videler, H., Runswick, M.J., Walker, J.E., Neuhaus, D.(2001) J Mol Biology 308: 325-339
- PubMed: 11327770
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2001.4570
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1HF9 - PubMed Abstract:
Bovine IF(1) is a basic, 84 amino acid residue protein that inhibits the hydrolytic action of the F(1)F(0) ATP synthase in mitochondria under anaerobic conditions. Its oligomerization state is dependent on pH. At a pH value below 6.5 it forms an active dimer. At higher pH values, two dimers associate to form an inactive tetramer. Here, we present the solution structure of a C-terminal fragment of IF(1) (44-84) containing all five of the histidine residues present in the sequence. Most unusually, the molecule forms an anti-parallel coiled-coil in which three of the five histidine residues occupy key positions at the dimer interface.
Organizational Affiliation:
MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Hills Road, Cambridge, CB2 2QH, UK.