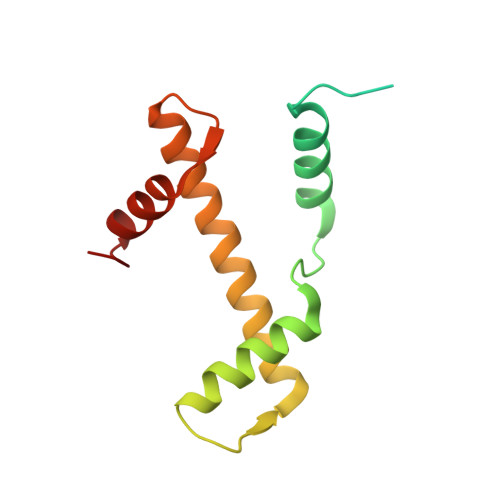
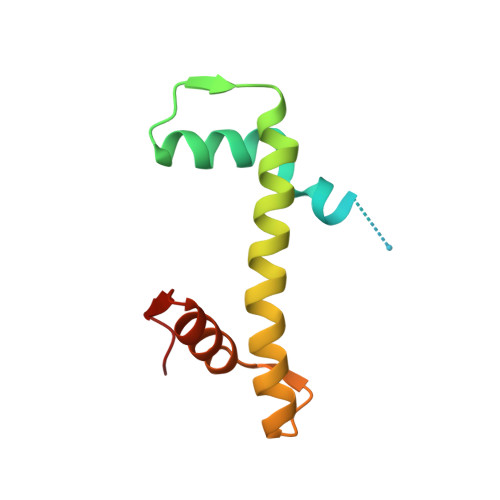
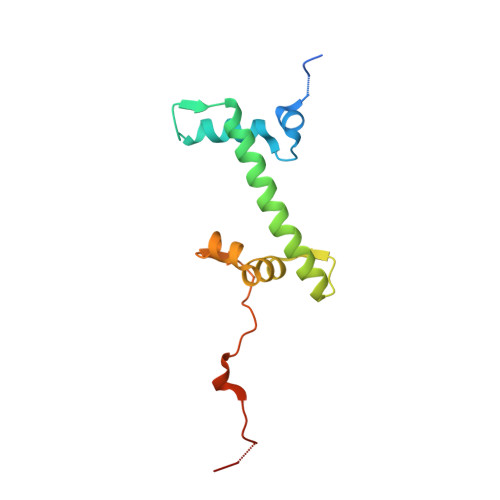
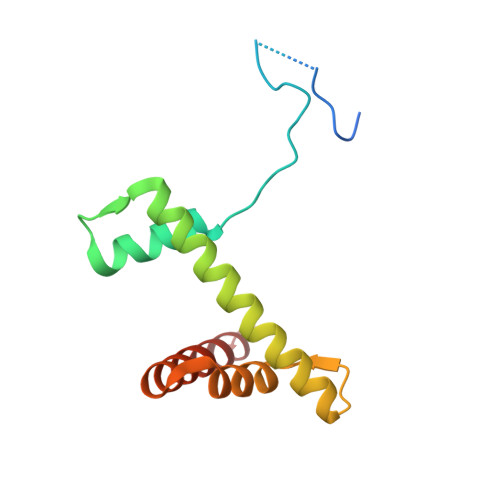
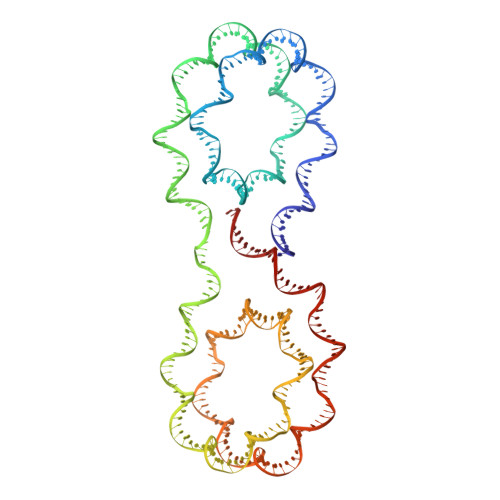
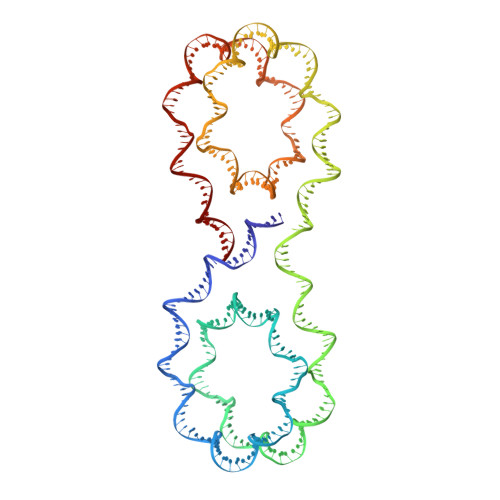
X-ray structure of a tetranucleosome and its implications for the chromatin fibre.
Schalch, T., Duda, S., Sargent, D.F., Richmond, T.J.(2005) Nature 436: 138-141
- PubMed: 16001076
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03686
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ZBB - PubMed Abstract:
DNA in eukaryotic chromosomes is organized in arrays of nucleosomes compacted into chromatin fibres. This higher-order structure of nucleosomes is the substrate for DNA replication, recombination, transcription and repair. Although the structure of the nucleosome core is known at near-atomic resolution, even the most fundamental information about the organization of nucleosomes in the fibre is controversial. Here we report the crystal structure of an oligonucleosome (a compact tetranucleosome) at 9 A resolution, solved by molecular replacement using the nucleosome core structure. The structure shows that linker DNA zigzags back and forth between two stacks of nucleosome cores, which form a truncated two-start helix, and does not follow a path compatible with a one-start solenoidal helix. The length of linker DNA is most probably buffered by stretching of the DNA contained in the nucleosome cores. We have built continuous fibre models by successively stacking tetranucleosomes one on another. The resulting models are nearly fully compacted and most closely resemble the previously described crossed-linker model. They suggest that the interfaces between nucleosomes along a single helix start are polymorphic.
Organizational Affiliation:
ETH Zürich, Institute for Molecular Biology and Biophysics, ETH-Hönggerberg, CH-8093 Zürich, Switzerland.