Computational redesign of protein-protein interaction specificity
Kortemme, T., Joachimiak, L.A., Bullock, A.N., Schuler, A.D., Stoddard, B.L., Baker, D.(2004) Nat Struct Mol Biol 11: 371-379
- PubMed: 15034550
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb749
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
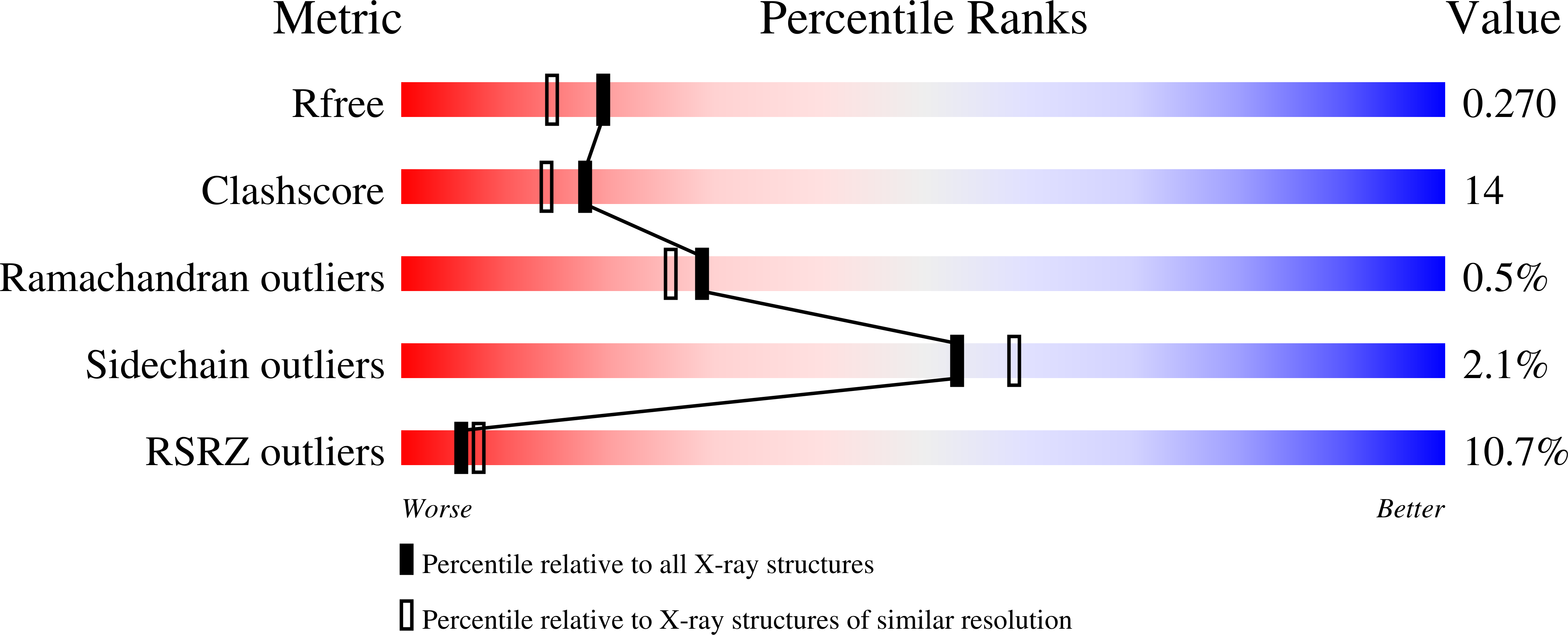
1UJZ - PubMed Abstract:
We developed a 'computational second-site suppressor' strategy to redesign specificity at a protein-protein interface and applied it to create new specifically interacting DNase-inhibitor protein pairs. We demonstrate that the designed switch in specificity holds in in vitro binding and functional assays. We also show that the designed interfaces are specific in the natural functional context in living cells, and present the first high-resolution X-ray crystallographic analysis of a computer-redesigned functional protein-protein interface with altered specificity. The approach should be applicable to the design of interacting protein pairs with novel specificities for delineating and re-engineering protein interaction networks in living cells.
Organizational Affiliation:
Howard Hughes Medical Institute & Department of Biochemistry, Box 357350, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington 98195-7350, USA.