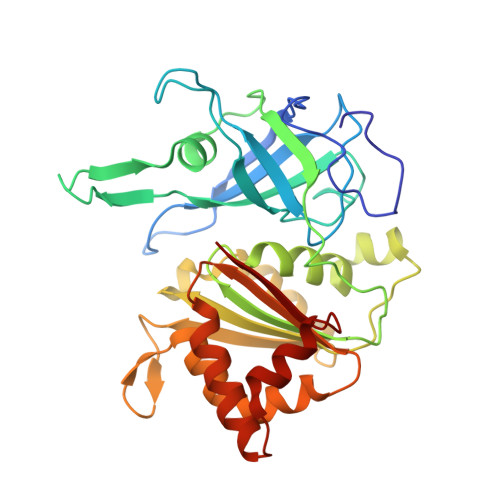
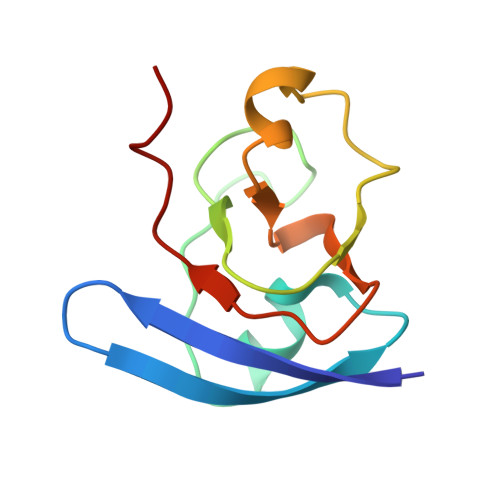
Crystallographic studies of the interaction between the ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase and ferredoxin from the cyanobacterium Anabaena: looking for the elusive ferredoxin molecule.
Morales, R., Kachalova, G., Vellieux, F., Charon, M.H., Frey, M.(2000) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 56: 1408-1412
- PubMed: 11053838
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/s0907444900010052
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1EWY - PubMed Abstract:
Ferredoxin-NADP(+) reductase (FNR) and its physiological electron donor ferredoxin (Fd) from the cyanobacterium Anabaena PCC7119 have been co-crystallized. The unit-cell parameters are a = b = 63.72, c = 158.02 A and the space group is P2(1)2(1)2(1). The crystal structure has been solved with 2.4 A resolution synchrotron data by molecular replacement, anomalous dispersion and R(min) search methods. For the computations, the crystal was treated as a merohedral twin. The asymmetric unit contains two FNR molecules and one ferredoxin molecule. The packing of the FNR molecules displays a nearly tetragonal symmetry (space group P4(3)2(1)2), whereas the ferredoxin arrangement is orthorhombic. This study provides the first crystallographic model of a dissociable complex between FNR and Fd.
Organizational Affiliation:
LCCP, Institut de Biologie Structurale J. P. Ebel, CEA-CNRS, 41 Rue Jules Horowitz, F38027 Grenoble, France.