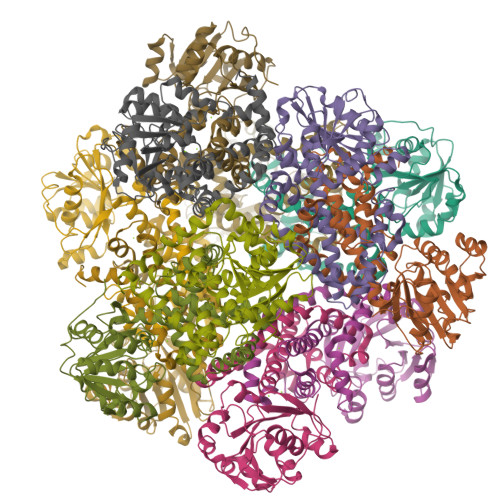
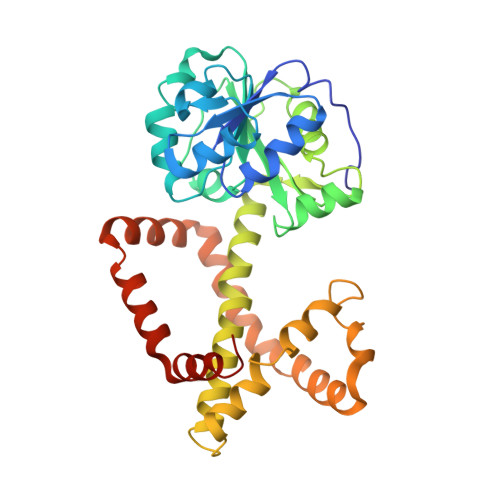
Use of Cryo-EM To Uncover Structural Bases of pH Effect and Cofactor Bispecificity of Ketol-Acid Reductoisomerase.
Chen, C.Y., Chang, Y.C., Lin, B.L., Lin, K.F., Huang, C.H., Hsieh, D.L., Ko, T.P., Tsai, M.D.(2019) J Am Chem Soc 141: 6136-6140
- PubMed: 30921515
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b01354
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6JCV, 6JCW, 6JCZ, 6JD1, 6JD2 - PubMed Abstract:
While cryo-EM is revolutionizing structural biology, its impact on enzymology is yet to be fully demonstrated. The ketol-acid reductoisomerase (KARI) catalyzes conversion of (2 S)-acetolactate or (2 S)-aceto-2-hydroxybutyrate to 2,3-dihydroxy-3-alkylbutyrate. We found that KARI from archaea Sulfolobus solfataricus (Sso-KARI) is unusual in being a dodecamer, bispecific to NADH and NADPH, and losing activity above pH 7.8. While crystals were obtainable only at pH 8.5, cryo-EM structures were solved at pH 7.5 and 8.5 for Sso-KARI:2Mg 2+ . The results showed that the distances of the two catalytic Mg 2+ ions are lengthened in both structures at pH 8.5. We next solved cryo-EM structures of two Sso-KARI complexes, with NADH+inhibitor and NADPH+inhibitor at pH 7.5, which indicate that the bispecificity can be attributed to a unique asparagine at the cofactor binding loop. Unexpectedly, Sso-KARI also differs from other KARI enzymes in lacking "induced-fit", reflecting structural rigidity. Thus, cryo-EM is powerful for structural and mechanistic enzymology.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Life Sciences , National Central University , Taoyuan 32001 , Taiwan.