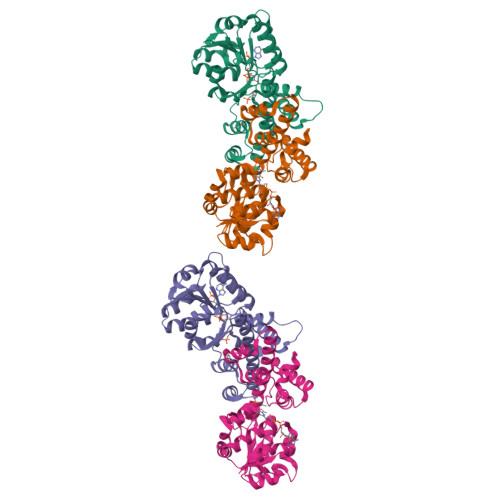Characterization of Two Late-Stage Enzymes Involved in Fosfomycin Biosynthesis in Pseudomonads.
Olivares, P., Ulrich, E.C., Chekan, J.R., van der Donk, W.A., Nair, S.K.(2017) ACS Chem Biol 12: 456-463
- PubMed: 27977135
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.6b00939
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5U55, 5U57, 5U58, 5U5D, 5U5G - PubMed Abstract:
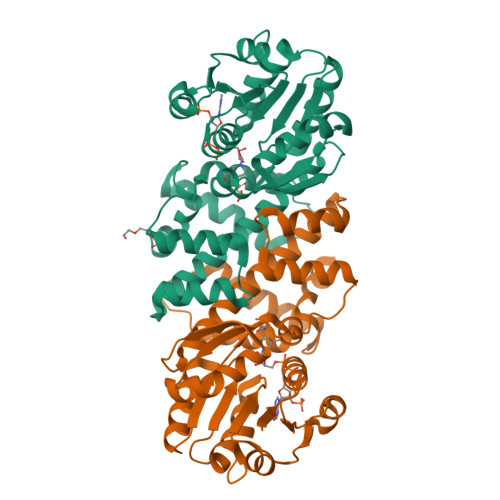
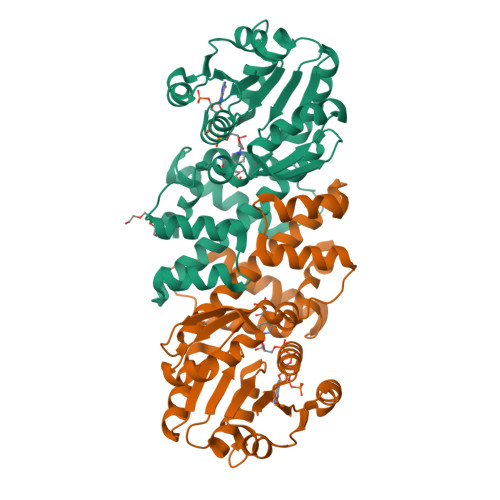
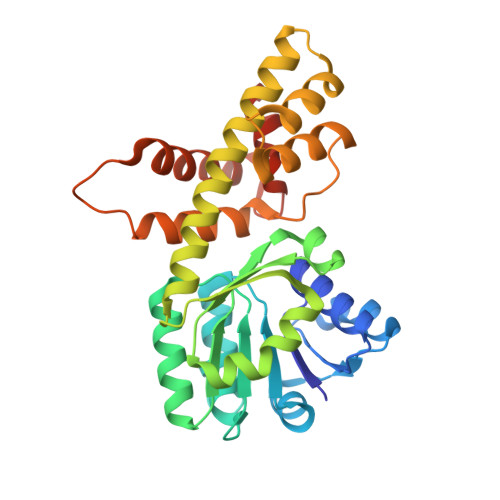
The broad-spectrum phosphonate antibiotic fosfomycin is currently in use for clinical treatment of infections caused by both Gram-positive and Gram-negative uropathogens. The antibiotic is biosynthesized by various streptomycetes, as well as by pseudomonads. Notably, the biosynthetic strategies used by the two genera share only two steps: the first step in which primary metabolite phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) is converted to phosphonopyruvate (PnPy) and the terminal step in which 2-hydroxypropylphosphonate (2-HPP) is converted to fosfomycin. Otherwise, distinct enzymatic paths are employed. Here, we biochemically confirm the last two steps in the fosfomycin biosynthetic pathway of Pseudomonas syringae PB-5123, showing that Psf3 performs the reduction of 2-oxopropylphosphonate (2-OPP) to (S)-2-HPP, followed by the Psf4-catalyzed epoxidation of (S)-2-HPP to fosfomycin. Psf4 can also accept (R)-2-HPP as a substrate but instead performs an oxidation to make 2-OPP. We show that the combined activities of Psf3 and Psf4 can be used to convert racemic 2-HPP to fosfomycin in an enantioconvergent process. X-ray structures of each enzyme with bound substrates provide insights into the stereospecificity of each conversion. These studies shed light on the reaction mechanisms of the two terminal enzymes in a distinct pathway employed by pseudomonads for the production of a potent antimicrobial agent.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, ‡Department of Chemistry, §Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology, ∥Howard Hughes Medical Institute, and ⊥Center for Biophysics and Computational Biology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign , Urbana, Illinois 61801, United States.