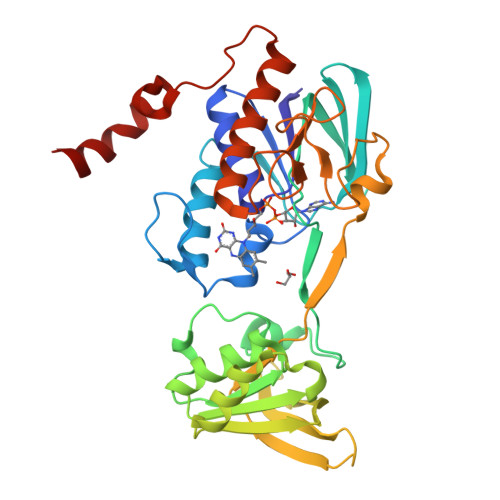
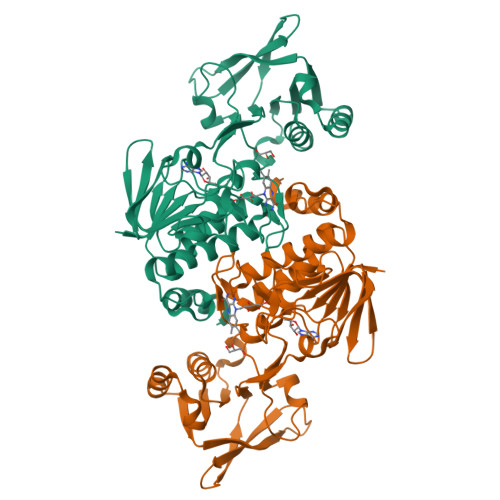
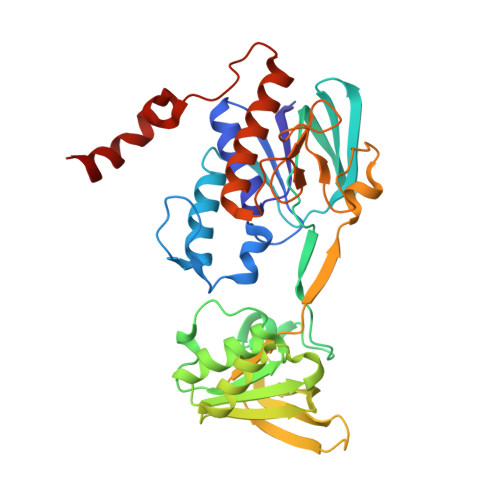
Iron Uptake Oxidoreductase (IruO) Uses a Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide Semiquinone Intermediate for Iron-Siderophore Reduction.
Kobylarz, M.J., Heieis, G.A., Loutet, S.A., Murphy, M.E.P.(2017) ACS Chem Biol 12: 1778-1786
- PubMed: 28463500
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.7b00203
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5TWB, 5TWC - PubMed Abstract:
Many pathogenic bacteria including Staphylococcus aureus use iron-chelating siderophores to acquire iron. Iron uptake oxidoreductase (IruO), a flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)-containing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)-dependent reductase from S. aureus, functions as a reductase for IsdG and IsdI, two paralogous heme degrading enzymes. Also, the gene encoding for IruO was shown to be required for growth of S. aureus on hydroxamate siderophores as a sole iron source. Here, we show that IruO binds the hydroxamate-type siderophores desferrioxamine B and ferrichrome A with low micromolar affinity and in the presence of NADPH, Fe(II) was released. Steady-state kinetics of Fe(II) release provides k cat /K m values in the range of 600 to 7000 M -1 s -1 for these siderophores supporting a role for IruO as a siderophore reductase in iron utilization. Crystal structures of IruO were solved in two distinct conformational states mediated by the formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond. A putative siderophore binding site was identified adjacent to the FAD cofactor. This site is partly occluded in the oxidized IruO structure consistent with this form being less active than reduced IruO. This reduction in activity could have a physiological role to limit iron release under oxidative stress conditions. Visible spectroscopy of anaerobically reduced IruO showed that the reaction proceeds by a single electron transfer mechanism through an FAD semiquinone intermediate. From the data, a model for single electron siderophore reduction by IruO using NADPH is described.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Life Sciences Institute, University of British Columbia , Vancouver, British Columbia V6T 1Z3; Canada.