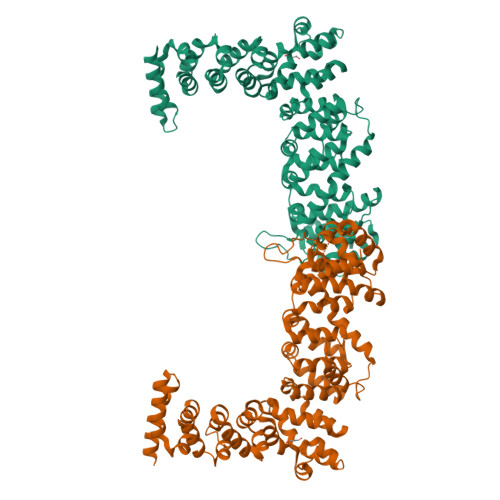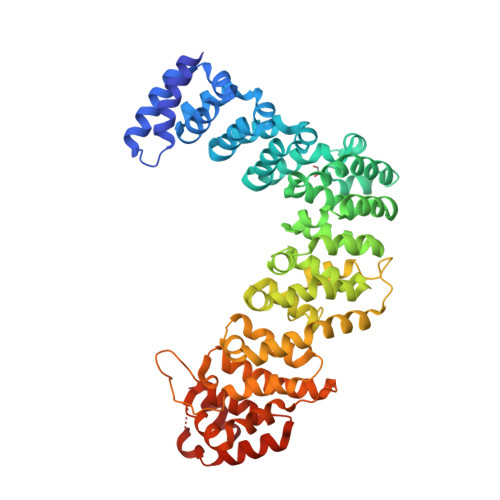A divergent Pumilio repeat protein family for pre-rRNA processing and mRNA localization.
Qiu, C., McCann, K.L., Wine, R.N., Baserga, S.J., Hall, T.M.(2014) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111: 18554-18559
- PubMed: 25512524
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1407634112
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4WZR, 4WZW - PubMed Abstract:
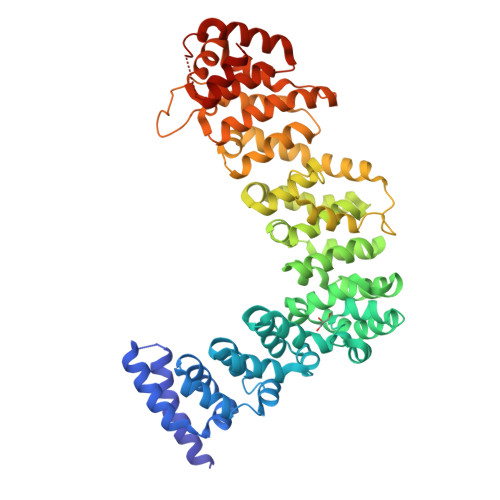
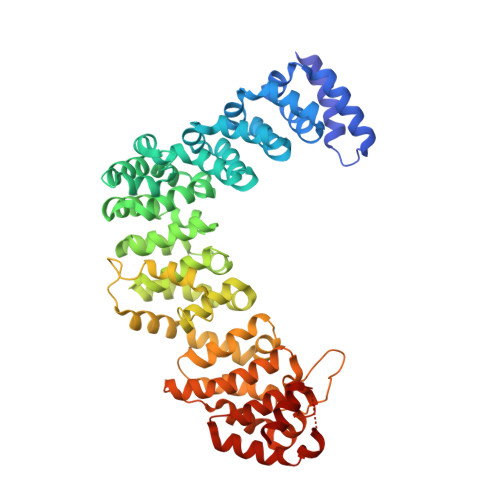
Pumilio/feminization of XX and XO animals (fem)-3 mRNA-binding factor (PUF) proteins bind sequence specifically to mRNA targets using a single-stranded RNA-binding domain comprising eight Pumilio (PUM) repeats. PUM repeats have now been identified in proteins that function in pre-rRNA processing, including human Puf-A and yeast Puf6. This is a role not previously ascribed to PUF proteins. Here we present crystal structures of human Puf-A that reveal a class of nucleic acid-binding proteins with 11 PUM repeats arranged in an "L"-like shape. In contrast to classical PUF proteins, Puf-A forms sequence-independent interactions with DNA or RNA, mediated by conserved basic residues. We demonstrate that equivalent basic residues in yeast Puf6 are important for RNA binding, pre-rRNA processing, and mRNA localization. Thus, PUM repeats can be assembled into alternative folds that bind to structured nucleic acids in addition to forming canonical eight-repeat crescent-shaped RNA-binding domains found in classical PUF proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Epigenetics and Stem Cell Biology Laboratory, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709; and.