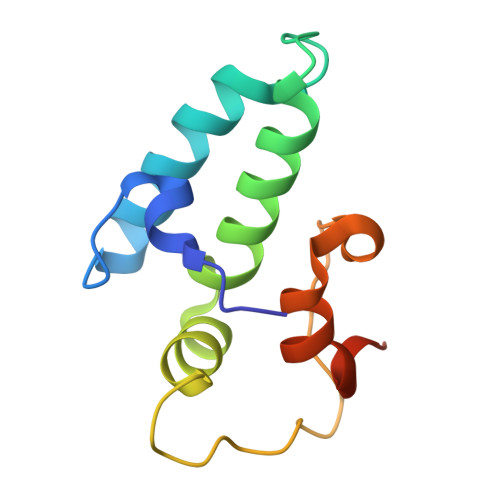
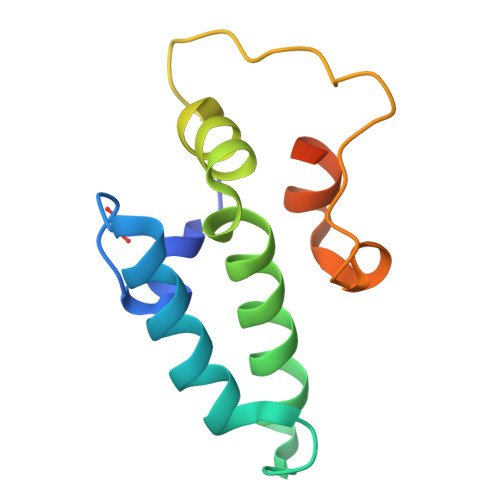
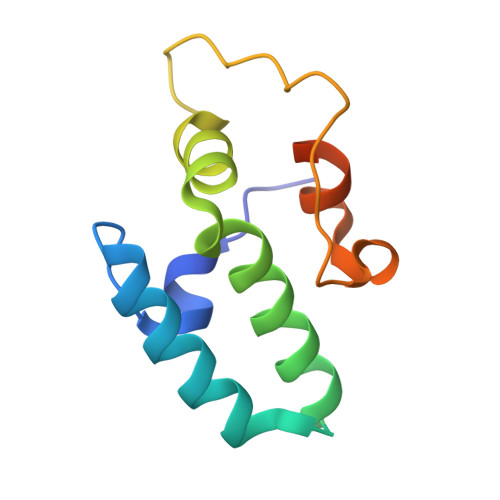
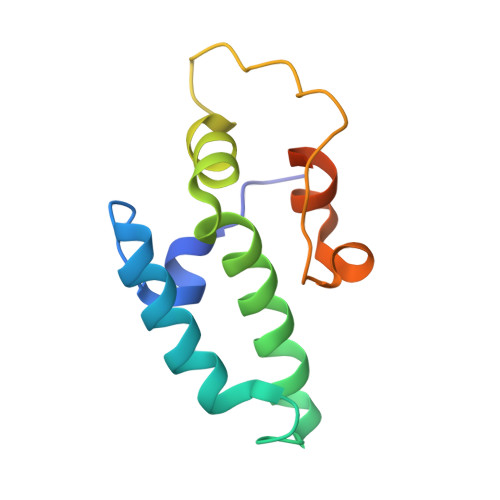
Combining crystallography and EPR: crystal and solution structures of the multidomain cochaperone DnaJ.
Barends, T.R., Brosi, R.W., Steinmetz, A., Scherer, A., Hartmann, E., Eschenbach, J., Lorenz, T., Seidel, R., Shoeman, R.L., Zimmermann, S., Bittl, R., Schlichting, I., Reinstein, J.(2013) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 69: 1540-1552
- PubMed: 23897477
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444913010640
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4J7Z, 4J80 - PubMed Abstract:
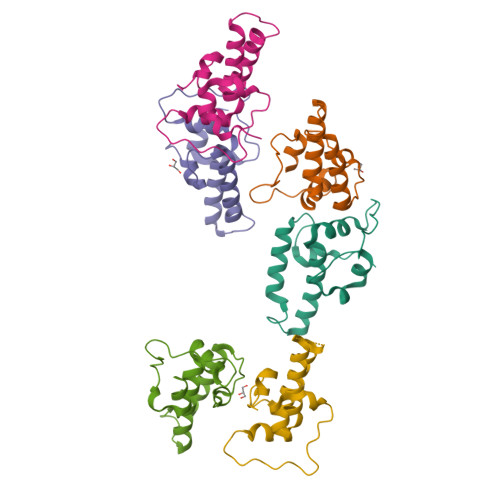
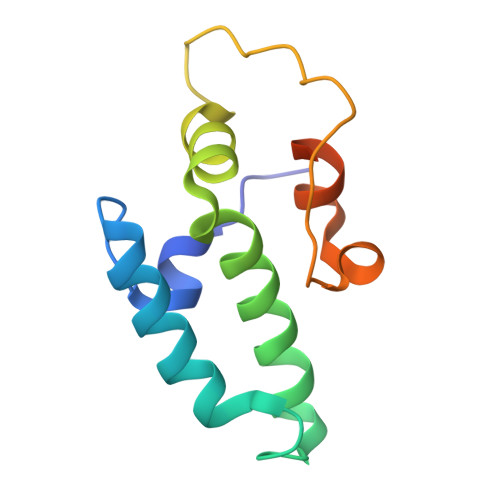
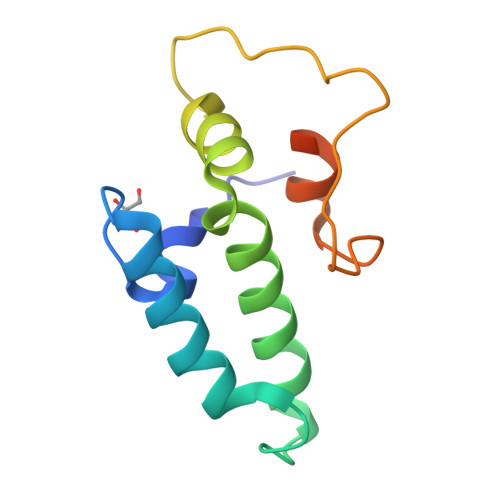
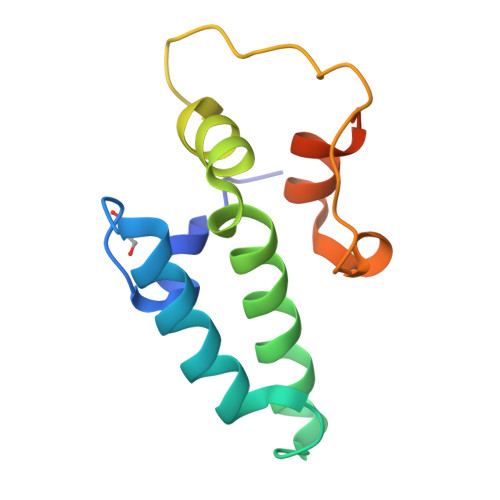
Hsp70 chaperones assist in a large variety of protein-folding processes in the cell. Crucial for these activities is the regulation of Hsp70 by Hsp40 cochaperones. DnaJ, the bacterial homologue of Hsp40, stimulates ATP hydrolysis by DnaK (Hsp70) and thus mediates capture of substrate protein, but is also known to possess chaperone activity of its own. The first structure of a complete functional dimeric DnaJ was determined and the mobility of its individual domains in solution was investigated. Crystal structures of the complete molecular cochaperone DnaJ from Thermus thermophilus comprising the J, GF and C-terminal domains and of the J and GF domains alone showed an ordered GF domain interacting with the J domain. Structure-based EPR spin-labelling studies as well as cross-linking results showed the existence of multiple states of DnaJ in solution with different arrangements of the various domains, which has implications for the function of DnaJ.
Organizational Affiliation:
MPI for Medical Research, Heidelberg, Germany. thomas.barends@mpimf-heidelberg.mpg.de