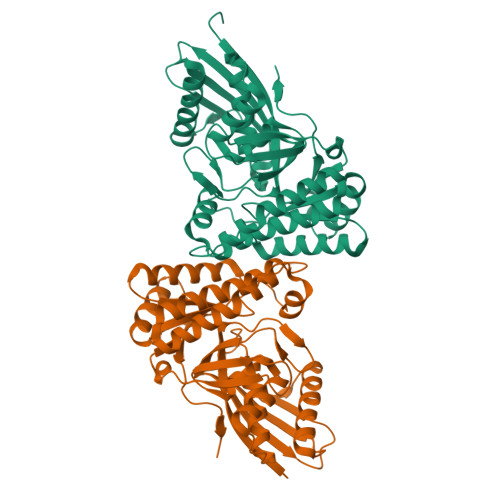
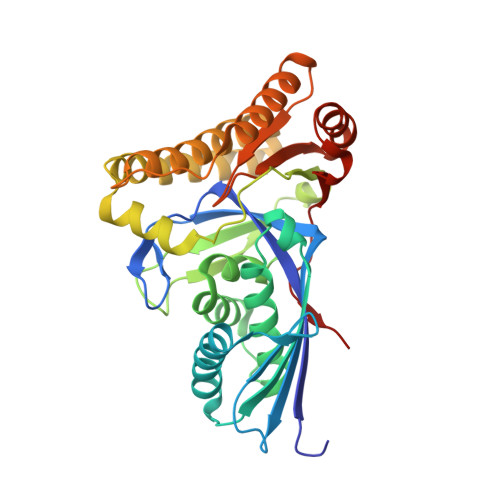
Crystal structures of Staphylococcus epidermidis mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase bound to inhibitory analogs reveal new insight into substrate binding and catalysis.
Barta, M.L., Skaff, D.A., McWhorter, W.J., Herdendorf, T.J., Miziorko, H.M., Geisbrecht, B.V.(2011) J Biological Chem 286: 23900-23910
- PubMed: 21561869
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.242016
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3QT5, 3QT6, 3QT7, 3QT8 - PubMed Abstract:
The polyisoprenoid compound undecaprenyl phosphate is required for biosynthesis of cell wall peptidoglycans in gram-positive bacteria, including pathogenic Enterococcus, Streptococcus, and Staphylococcus spp. In these organisms, the mevalonate pathway is used to produce the precursor isoprenoid, isopentenyl 5-diphosphate. Mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase (MDD) catalyzes formation of isopentenyl 5-diphosphate in an ATP-dependent irreversible reaction and is therefore an attractive target for inhibitor development that could lead to new antimicrobial agents. To facilitate exploration of this possibility, we report the crystal structure of Staphylococcus epidermidis MDD (1.85 Å resolution) and, to the best of our knowledge, the first structures of liganded MDD. These structures include MDD bound to the mevalonate 5-diphosphate analogs diphosphoglycolyl proline (2.05 Å resolution) and 6-fluoromevalonate diphosphate (FMVAPP; 2.2 Å resolution). Comparison of these structures provides a physical basis for the significant differences in K(i) values observed for these inhibitors. Inspection of enzyme/inhibitor structures identified the side chain of invariant Ser(192) as making potential contributions to catalysis. Significantly, Ser → Ala substitution of this side chain decreases k(cat) by ∼10(3)-fold, even though binding interactions between FMVAPP and this mutant are similar to those observed with wild type MDD, as judged by the 2.1 Å cocrystal structure of S192A with FMVAPP. Comparison of microbial MDD structures with those of mammalian counterparts reveals potential targets at the active site periphery that may be exploited to selectively target the microbial enzymes. These studies provide a structural basis for previous observations regarding the MDD mechanism and inform future work toward rational inhibitor design.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Cell Biology and Biophysics, School of Biological Sciences, University of Missouri-Kansas City, Kansas City, Missouri 64110, USA.