Structure of l-aspartate oxidase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus tokodaii
Sakuraba, H., Yoneda, K., Asai, I., Tsuge, H., Katunuma, N., Ohshima, T.(2008) Biochim Biophys Acta 1784: 563-571
- PubMed: 18226609
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.12.012
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2E5V - PubMed Abstract:
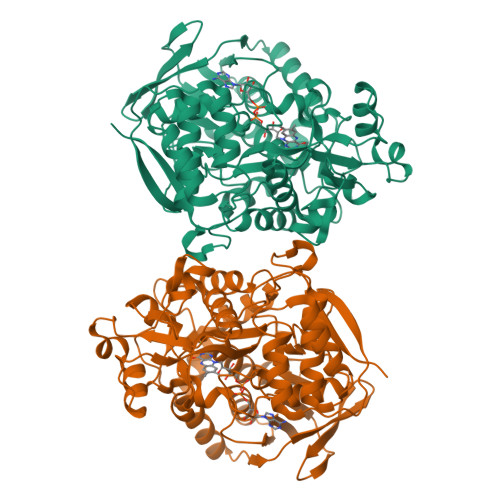
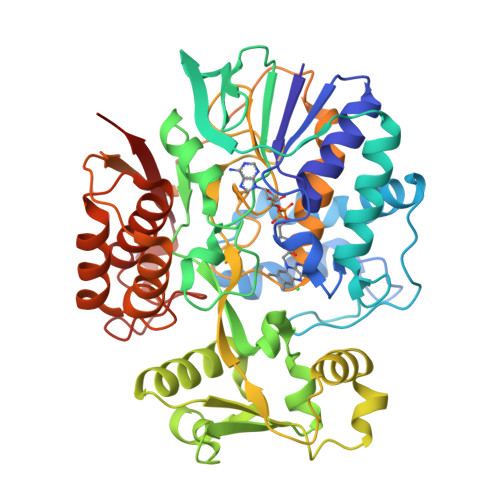
The crystal structure of the highly thermostable l-aspartate oxidase (LAO) from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus tokodaii was determined at a 2.09 A resolution. The factors contributing to the thermostability of the enzyme were analyzed by comparing its structure to that of Escherichia coli LAO. Like E. coli LAO, the S. tokodaii enzyme consists of three domains: an FAD-binding domain, an alpha+beta capping domain, and a C-terminal three-helix bundle. However, the situation of the linker between the FAD-binding domain and C-terminal three-helix bundle in S. tokodaii LAO is completely different from that in E. coli LAO, where the linker is situated near the FAD-binding domain and has virtually no interaction with the rest of the protein. In S. tokodaii LAO, this linker is situated near the C-terminal three-helix bundle and contains a beta-strand that runs parallel to the C-terminal strand. This results in the formation of an additional beta-sheet, which appears to reduce the flexibility of the C-terminal region. Furthermore, the displacement of the linker enables formation of a 5-residue ion-pair network between the FAD-binding and C-terminal domains, which strengthens the interdomain interactions. These features might be the main factors contributing to the high thermostability of S. tokodaii LAO.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Life System, Institute of Technology and Science, The University of Tokushima, 2-1 Minamijosanjima-cho, Tokushima 770-8506, Japan.