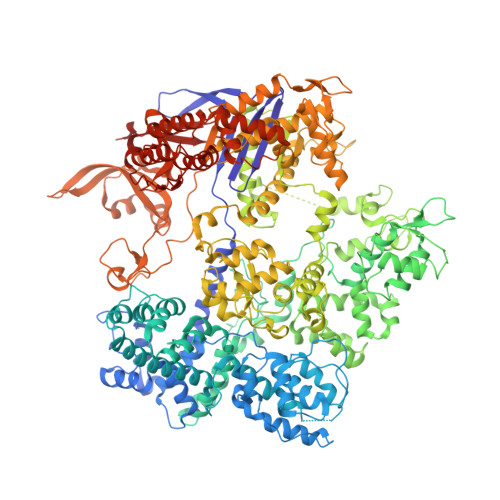
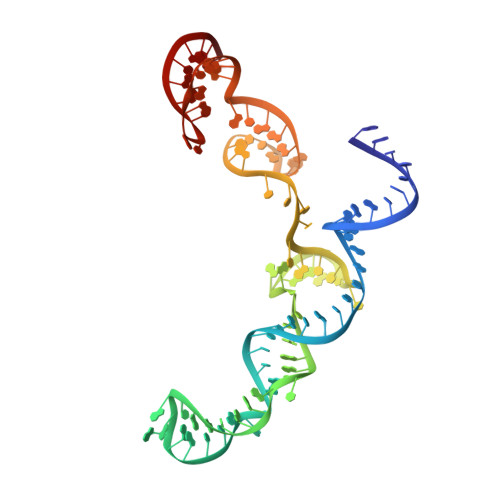
Unraveling the mechanisms of PAMless DNA interrogation by SpRY-Cas9.
Hibshman, G.N., Bravo, J.P.K., Hooper, M.M., Dangerfield, T.L., Zhang, H., Finkelstein, I.J., Johnson, K.A., Taylor, D.W.(2024) Nat Commun 15: 3663-3663
- PubMed: 38688943
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-47830-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8SPQ, 8SQH, 8SRS, 8T6O, 8T6P, 8T6S, 8T6T, 8T6X, 8T6Y, 8T76, 8T77, 8T78, 8T79, 8T7S, 8TZZ, 8U3Y - PubMed Abstract:
CRISPR-Cas9 is a powerful tool for genome editing, but the strict requirement for an NGG protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM) sequence immediately next to the DNA target limits the number of editable genes. Recently developed Cas9 variants have been engineered with relaxed PAM requirements, including SpG-Cas9 (SpG) and the nearly PAM-less SpRY-Cas9 (SpRY). However, the molecular mechanisms of how SpRY recognizes all potential PAM sequences remains unclear. Here, we combine structural and biochemical approaches to determine how SpRY interrogates DNA and recognizes target sites. Divergent PAM sequences can be accommodated through conformational flexibility within the PAM-interacting region, which facilitates tight binding to off-target DNA sequences. Nuclease activation occurs ~1000-fold slower than for Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9, enabling us to directly visualize multiple on-pathway intermediate states. Experiments with SpG position it as an intermediate enzyme between Cas9 and SpRY. Our findings shed light on the molecular mechanisms of PAMless genome editing.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biosciences, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, 78712, USA.