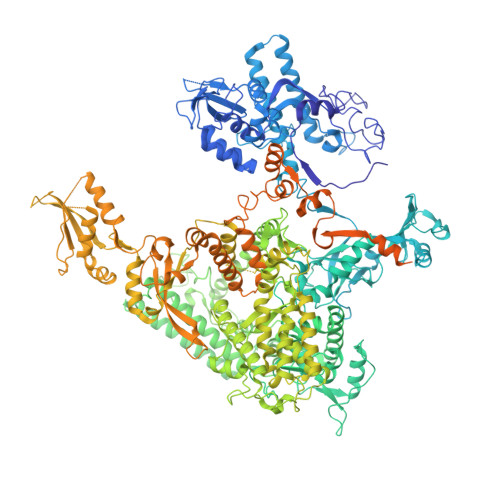
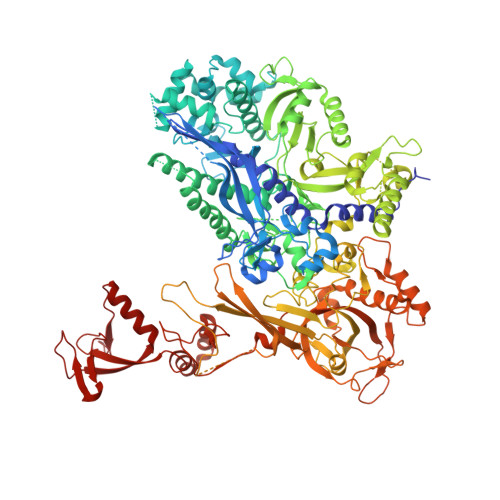
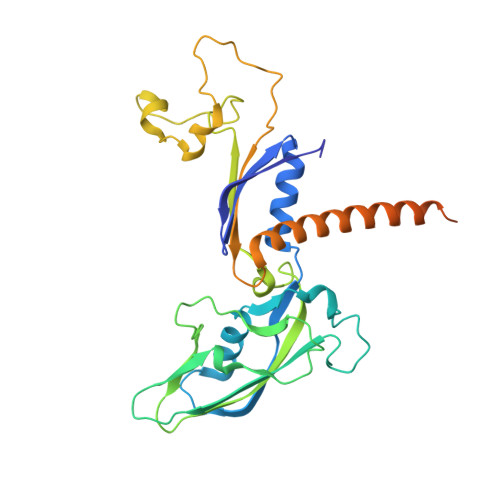
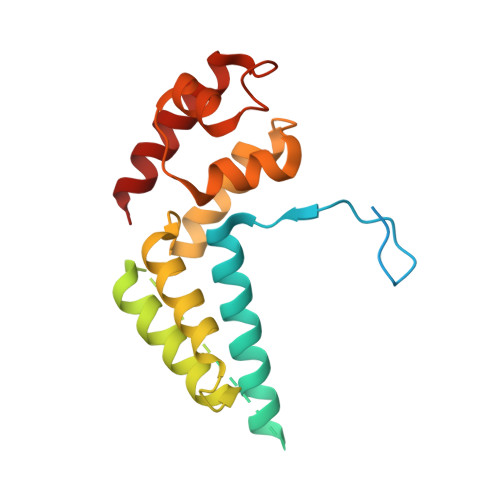
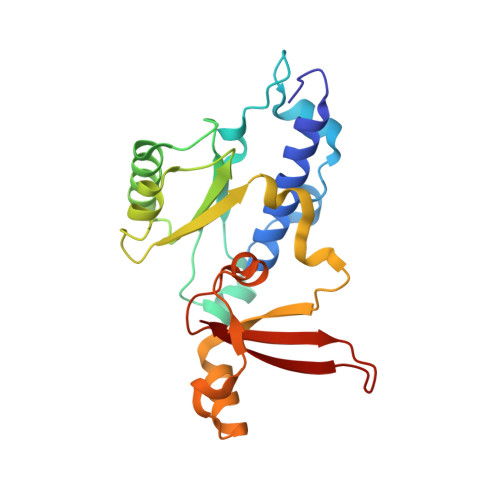
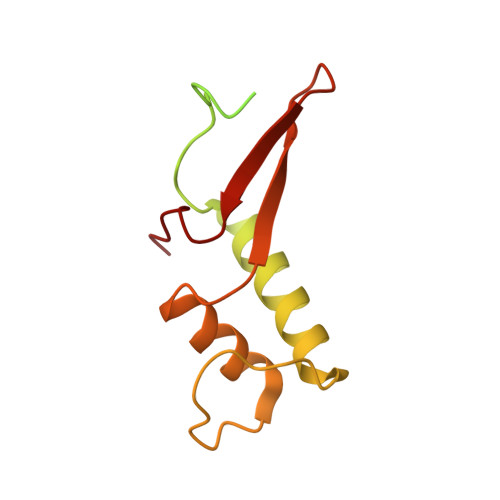
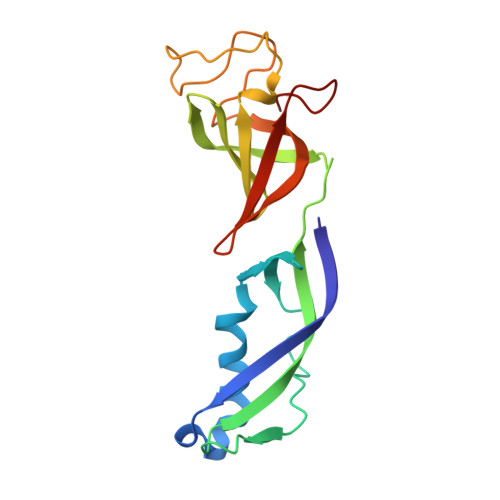
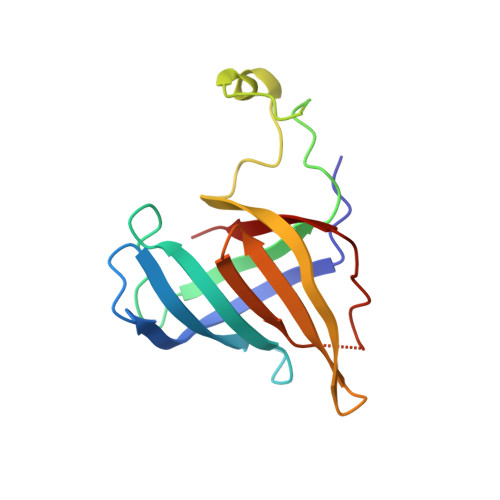
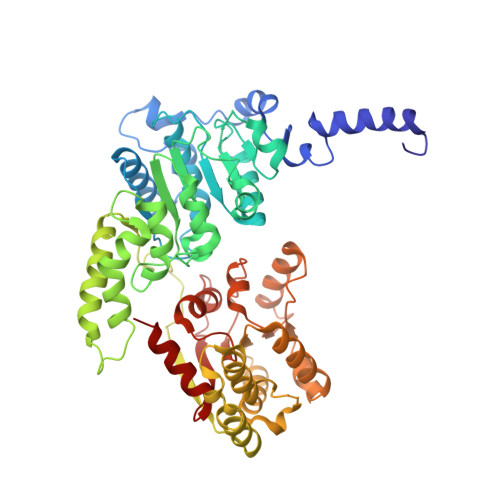
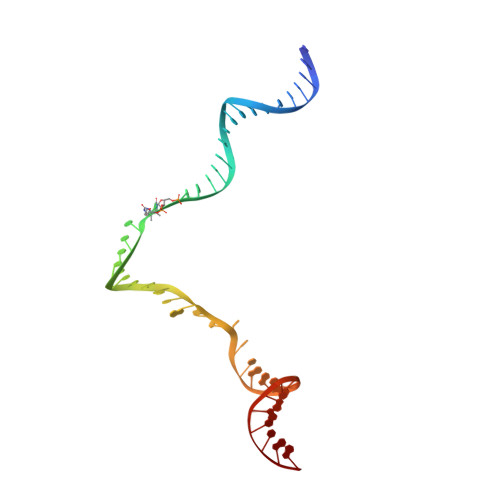
Elf1 promotes Rad26's interaction with lesion-arrested Pol II for transcription-coupled repair.
Sarsam, R.D., Xu, J., Lahiri, I., Gong, W., Li, Q., Oh, J., Zhou, Z., Hou, P., Chong, J., Hao, N., Li, S., Wang, D., Leschziner, A.E.(2024) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 121: e2314245121-e2314245121
- PubMed: 38194460
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2314245121
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8TUG, 8TVP, 8TVQ, 8TVS, 8TVV, 8TVW, 8TVX, 8TVY - PubMed Abstract:
Transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair (TC-NER) is a highly conserved DNA repair pathway that removes bulky lesions in the transcribed genome. Cockayne syndrome B protein (CSB), or its yeast ortholog Rad26, has been known for decades to play important roles in the lesion-recognition steps of TC-NER. Another conserved protein ELOF1, or its yeast ortholog Elf1, was recently identified as a core transcription-coupled repair factor. How Rad26 distinguishes between RNA polymerase II (Pol II) stalled at a DNA lesion or other obstacles and what role Elf1 plays in this process remains unknown. Here, we present cryo-EM structures of Pol II-Rad26 complexes stalled at different obstacles that show that Rad26 uses a common mechanism to recognize a stalled Pol II, with additional interactions when Pol II is arrested at a lesion. A cryo-EM structure of lesion-arrested Pol II-Rad26 bound to Elf1 revealed that Elf1 induces further interactions between Rad26 and a lesion-arrested Pol II. Biochemical and genetic data support the importance of the interplay between Elf1 and Rad26 in TC-NER initiation. Together, our results provide important mechanistic insights into how two conserved transcription-coupled repair factors, Rad26/CSB and Elf1/ELOF1, work together at the initial lesion recognition steps of transcription-coupled repair.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92093.