Design, Synthesis, X-ray Crystallography, and Biological Activities of Covalent, Non-Peptidic Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease.
Ashraf-Uz-Zaman, M., Chua, T.K., Li, X., Yao, Y., Moku, B.K., Mishra, C.B., Avadhanula, V., Piedra, P.A., Song, Y.(2024) ACS Infect Dis 10: 715-731
- PubMed: 38192109
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00565
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
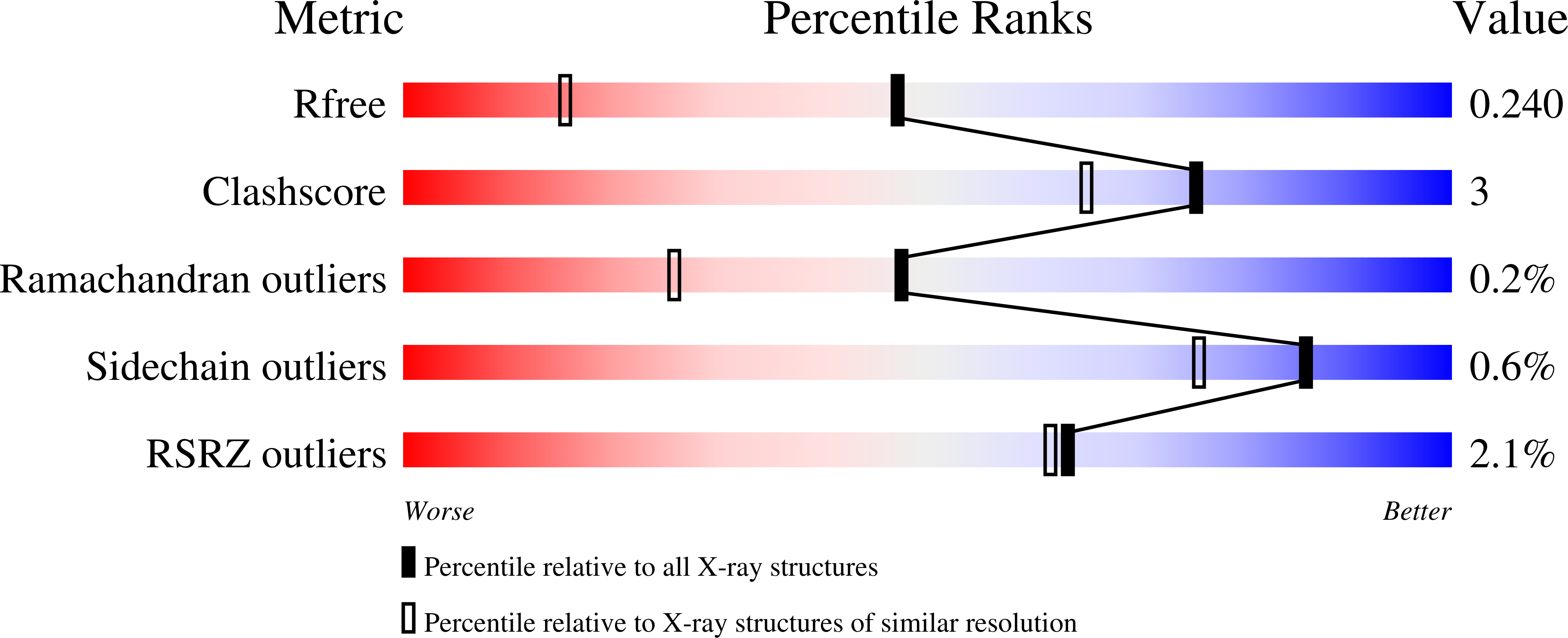
8TPB, 8TPC, 8TPD, 8TPE, 8TPF, 8TPG, 8TPH, 8TPI - PubMed Abstract:
Highly contagious SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus has infected billions of people worldwide with flu-like symptoms since its emergence in 2019. It has caused deaths of several million people. The viral main protease (Mpro) is essential for SARS-CoV-2 replication and therefore a drug target. Several series of covalent inhibitors of Mpro were designed and synthesized. Structure-activity relationship studies show that (1) several chloroacetamide- and epoxide-based compounds targeting Cys145 are potent inhibitors with IC 50 values as low as 0.49 μM and (2) Cys44 of Mpro is not nucleophilic for covalent inhibitor design. High-resolution X-ray studies revealed the protein-inhibitor interactions and mechanisms of inhibition. It is of interest that Cys145 preferably attacks the more hindered C α atom of several epoxide inhibitors. Chloroacetamide inhibitor 13 and epoxide inhibitor 30 were found to inhibit cellular SARS-CoV-2 replication with an EC 68 (half-log reduction of virus titer) of 3 and 5 μM. These compounds represent new pharmacological leads for anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug development.
Organizational Affiliation:
Verna and Marrs McLean Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, Baylor College of Medicine, 1 Baylor Plaza, Houston, Texas 77030, United States.