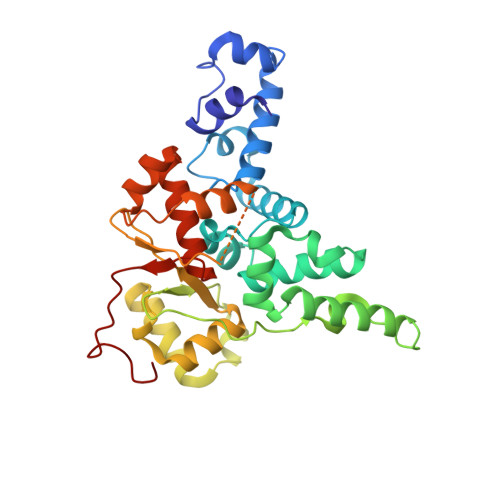
FAM91A1-TBC1D23 complex structure reveals human genetic variations susceptible for PCH.
Zhao, L., Deng, H., Yang, Q., Tang, Y., Zhao, J., Li, P., Zhang, S., Yong, X., Li, T., Billadeau, D.D., Jia, D.(2023) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 120: e2309910120-e2309910120
- PubMed: 37903274
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2309910120
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8JJ9 - PubMed Abstract:
Pontocerebellar hypoplasia (PCH) is a group of rare neurodevelopmental disorders with limited diagnostic and therapeutic options. Mutations in WDR11, a subunit of the FAM91A1 complex, have been found in patients with PCH-like symptoms; however, definitive evidence that the mutations are causal is still lacking. Here, we show that depletion of FAM91A1 results in developmental defects in zebrafish similar to that of TBC1D23, an established PCH gene. FAM91A1 and TBC1D23 directly interact with each other and cooperate to regulate endosome-to-Golgi trafficking of KIAA0319L, a protein known to regulate axonal growth. Crystal structure of the FAM91A1-TBC1D23 complex reveals that TBC1D23 binds to a conserved surface on FAM91A1 by assuming a Z-shaped conformation. More importantly, the interaction between FAM91A1 and TBC1D23 can be used to predict the risk of certain TBC1D23-associated mutations to PCH. Collectively, our study provides a molecular basis for the interaction between TBC1D23 and FAM91A1 and suggests that disrupted endosomal trafficking underlies multiple PCH subtypes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Key Laboratory of Birth Defects and Related Diseases of Women and Children, Department of Paediatrics, West China Second University Hospital, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Collaborative Innovation Center of Biotherapy, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China.