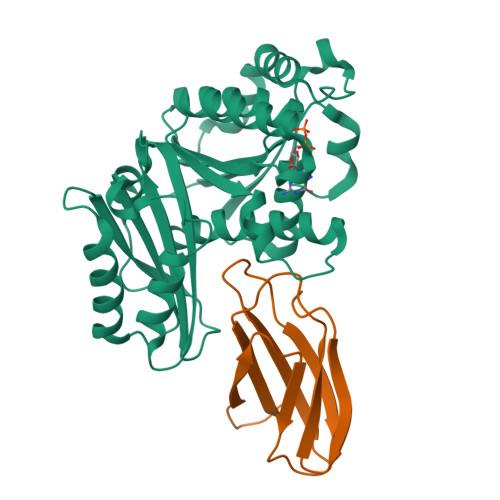
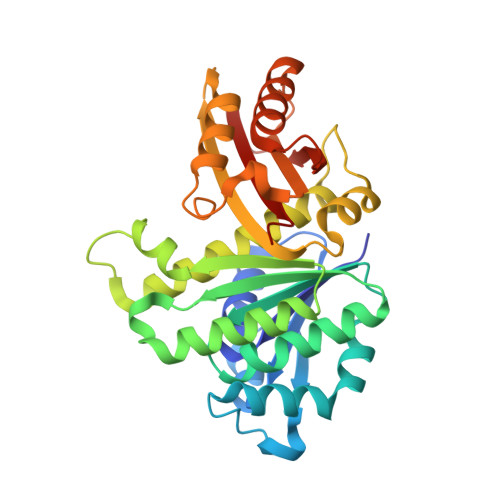
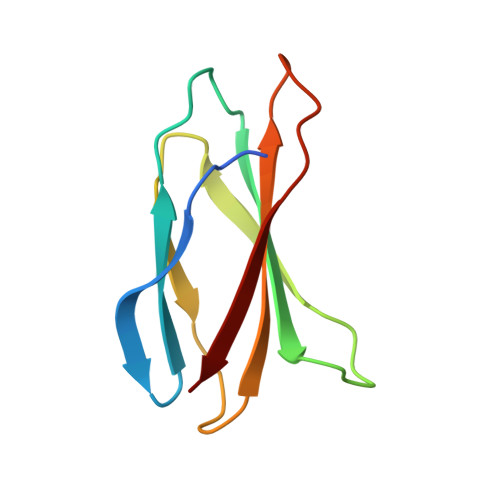
Structures of a FtsZ single protofilament and a double-helical tube in complex with a monobody.
Fujita, J., Amesaka, H., Yoshizawa, T., Hibino, K., Kamimura, N., Kuroda, N., Konishi, T., Kato, Y., Hara, M., Inoue, T., Namba, K., Tanaka, S.I., Matsumura, H.(2023) Nat Commun 14: 4073-4073
- PubMed: 37429870
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-39807-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8GZV, 8GZW, 8GZX, 8GZY, 8H1O, 8IBN - PubMed Abstract:
FtsZ polymerizes into protofilaments to form the Z-ring that acts as a scaffold for accessory proteins during cell division. Structures of FtsZ have been previously solved, but detailed mechanistic insights are lacking. Here, we determine the cryoEM structure of a single protofilament of FtsZ from Klebsiella pneumoniae (KpFtsZ) in a polymerization-preferred conformation. We also develop a monobody (Mb) that binds to KpFtsZ and FtsZ from Escherichia coli without affecting their GTPase activity. Crystal structures of the FtsZ-Mb complexes reveal the Mb binding mode, while addition of Mb in vivo inhibits cell division. A cryoEM structure of a double-helical tube of KpFtsZ-Mb at 2.7 Å resolution shows two parallel protofilaments. Our present study highlights the physiological roles of the conformational changes of FtsZ in treadmilling that regulate cell division.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Frontier Biosciences, Osaka University, 1-3 Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka, 565-0871, Japan.