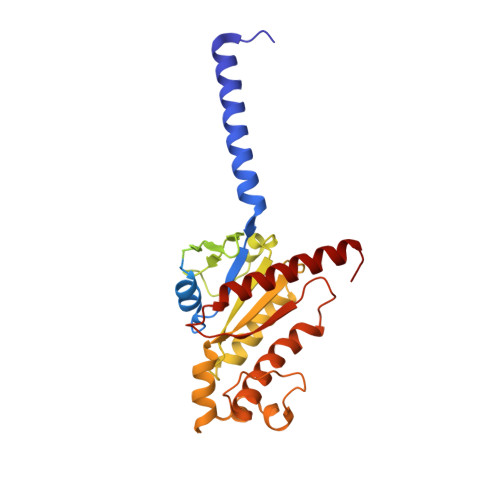
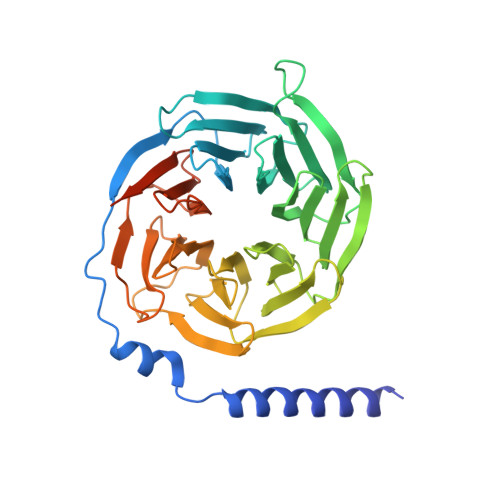
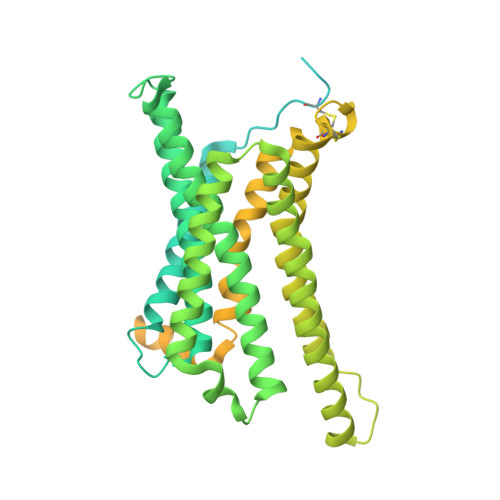
Structural basis of signaling regulation of the human melanocortin-2 receptor by MRAP1.
Luo, P., Feng, W., Ma, S., Dai, A., Wu, K., Chen, X., Yuan, Q., Cai, X., Yang, D., Wang, M.W., Eric Xu, H., Jiang, Y.(2023) Cell Res 33: 46-54
- PubMed: 36588120
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-022-00751-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8GY7 - PubMed Abstract:
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are regulated by various downstream proteins, of which the melanocortin receptor accessory protein 1 (MRAP1) is closely involved in the regulation of melanocortin receptor 2 (MC2R). Assisted by MRAP1, MC2R responds to adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and stimulates glucocorticoid biogenesis and cortisol secretion. MC2R activation plays an essential role in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis that regulates stress response, while its dysfunction causes glucocorticoid insufficiency- or cortisol excess-associated disorders. Here, we present a cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the ACTH-bound MC2R-G s -MRAP1 complex. Our structure, together with mutagenesis analysis, reveals a unique sharp kink at the extracellular region of MRAP1 and the 'seat-belt' effect of MRAP1 on stabilizing ACTH binding and MC2R activation. Mechanisms of ACTH recognition by MC2R and receptor activation are also demonstrated. These findings deepen our understanding of GPCR regulation by accessory proteins and provide valuable insights into the ab initio design of therapeutic agents targeting MC2R.
Organizational Affiliation:
The CAS Key Laboratory of Receptor Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China.