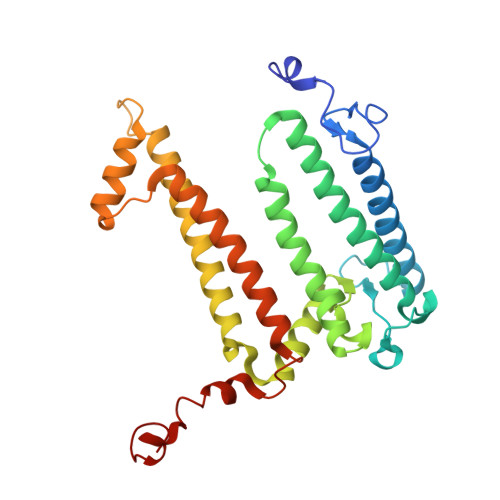
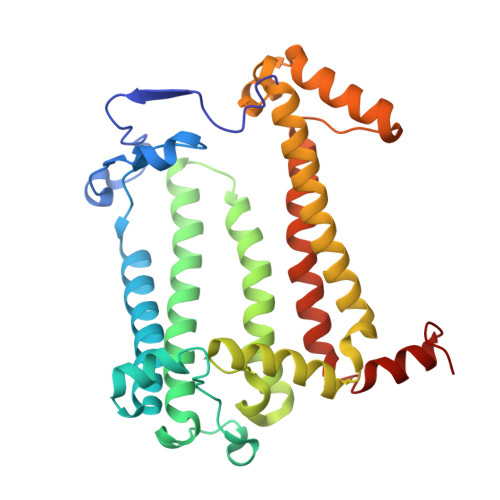
Cryo-EM structure of a monomeric RC-LH1-PufX supercomplex with high-carotenoid content from Rhodobacter capsulatus.
Bracun, L., Yamagata, A., Christianson, B.M., Shirouzu, M., Liu, L.N.(2023) Structure 31: 318
- PubMed: 36738736
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2023.01.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8B64 - PubMed Abstract:
In purple photosynthetic bacteria, the photochemical reaction center (RC) and light-harvesting complex 1 (LH1) assemble to form monomeric or dimeric RC-LH1 membrane complexes, essential for bacterial photosynthesis. Here, we report a 2.59-Å resolution cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the RC-LH1 supercomplex from Rhodobacter capsulatus. We show that Rba. capsulatus RC-LH1 complexes are exclusively monomers in which the RC is surrounded by a 15-subunit LH1 ring. Incorporation of a transmembrane polypeptide PufX leads to a large opening within the LH1 ring. Each LH1 subunit associates two carotenoids and two bacteriochlorophylls, which is similar to Rba. sphaeroides RC-LH1 but more than one carotenoid per LH1 in Rba. veldkampii RC-LH1 monomer. Collectively, the unique Rba. capsulatus RC-LH1-PufX represents an intermediate structure between Rba. sphaeroides and Rba. veldkampii RC-LH1-PufX. Comparison of PufX from the three Rhodobacter species indicates the important residues involved in dimerization of RC-LH1.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Systems, Molecular and Integrative Biology, University of Liverpool, Liverpool L69 7ZB, UK; Laboratory for Protein Functional and Structural Biology, RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research, 1-7-22 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi-ku, Yokohama, Kanagawa 230-0045, Japan.