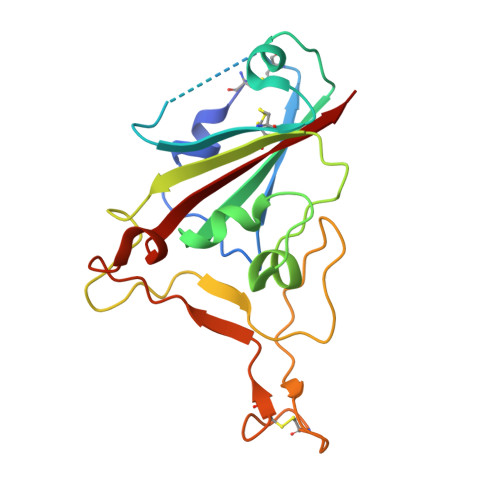
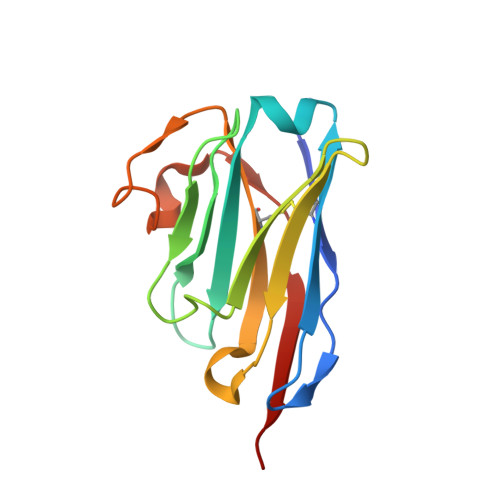
Nanobodies to multiple spike variants and inhalation of nanobody-containing aerosols neutralize SARS-CoV-2 in cell culture and hamsters.
Aksu, M., Kumar, P., Guttler, T., Taxer, W., Gregor, K., Mussil, B., Rymarenko, O., Stegmann, K.M., Dickmanns, A., Gerber, S., Reineking, W., Schulz, C., Henneck, T., Mohamed, A., Pohlmann, G., Ramazanoglu, M., Mese, K., Gross, U., Ben-Yedidia, T., Ovadia, O., Fischer, D.W., Kamensky, M., Reichman, A., Baumgartner, W., von Kockritz-Blickwede, M., Dobbelstein, M., Gorlich, D.(2023) Antiviral Res 221: 105778-105778
- PubMed: 38065245
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2023.105778
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8Q7S, 8Q93, 8Q94, 8Q95 - PubMed Abstract:
The ongoing threat of COVID-19 has highlighted the need for effective prophylaxis and convenient therapies, especially for outpatient settings. We have previously developed highly potent single-domain (VHH) antibodies, also known as nanobodies, that target the Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein and neutralize the Wuhan strain of the virus. In this study, we present a new generation of anti-RBD nanobodies with superior properties. The primary representative of this group, Re32D03, neutralizes Alpha to Delta as well as Omicron BA.2.75; other members neutralize, in addition, Omicron BA.1, BA.2, BA.4/5, and XBB.1. Crystal structures of RBD-nanobody complexes reveal how ACE2-binding is blocked and also explain the nanobodies' tolerance to immune escape mutations. Through the cryo-EM structure of the Ma16B06-BA.1 Spike complex, we demonstrated how a single nanobody molecule can neutralize a trimeric spike. We also describe a method for large-scale production of these nanobodies in Pichia pastoris, and for formulating them into aerosols. Exposing hamsters to these aerosols, before or even 24 h after infection with SARS-CoV-2, significantly reduced virus load, weight loss and pathogenicity. These results show the potential of aerosolized nanobodies for prophylaxis and therapy of coronavirus infections.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max Planck Institute for Multidisciplinary Sciences, Dept. of Cellular Logistics, Am Fassberg 11, 37077 Göttingen, Germany.