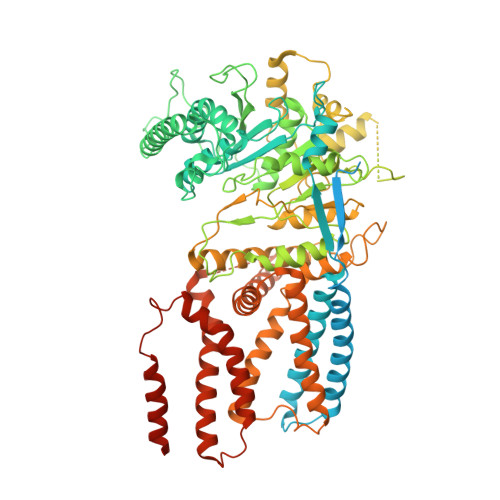
Insights into substrate coordination and glycosyl transfer of poplar cellulose synthase-8.
Verma, P., Kwansa, A.L., Ho, R., Yingling, Y.G., Zimmer, J.(2023) bioRxiv
- PubMed: 36798277
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.07.527505
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8G27, 8G2J - PubMed Abstract:
Cellulose is an abundant cell wall component of land plants. It is synthesized from UDP-activated glucose molecules by cellulose synthase, a membrane-integrated processive glycosyltransferase. Cellulose synthase couples the elongation of the cellulose polymer with its translocation across the plasma membrane. Here, we present substrate and product-bound cryogenic electron microscopy structures of the homotrimeric cellulose synthase isoform-8 (CesA8) from hybrid aspen (poplar). UDP-glucose binds to a conserved catalytic pocket adjacent to the entrance to a transmembrane channel. The substrate's glucosyl unit is coordinated by conserved residues of the glycosyltransferase domain and amphipathic interface helices. Site-directed mutagenesis of a conserved gating loop capping the active site reveals its critical function for catalytic activity. Molecular dynamics simulations reveal prolonged interactions of the gating loop with the substrate molecule, particularly across its central conserved region. These transient interactions likely facilitate the proper positioning of the substrate molecule for glycosyl transfer and cellulose translocation. Cryo-EM structures of substrate and product bound poplar cellulose synthase provide insights into substrate selectivitySite directed mutagenesis signifies a critical function of the gating loop for catalysisMolecular dynamics simulations support persistent gating loop - substrate interactionsGating loop helps in positioning the substrate molecule to facilitate cellulose elongationConserved cellulose synthesis substrate binding mechanism across the kingdoms.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Physiology and Biological Physics, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, 22903, USA.