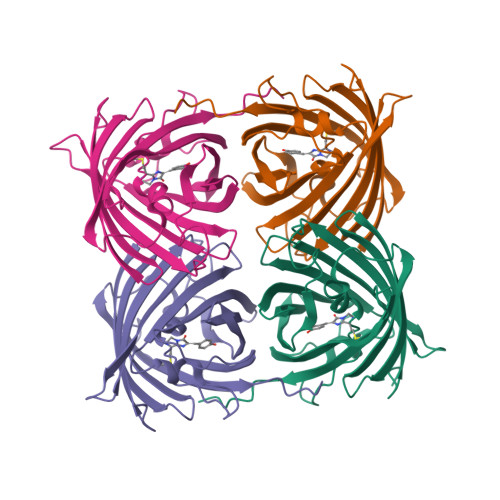
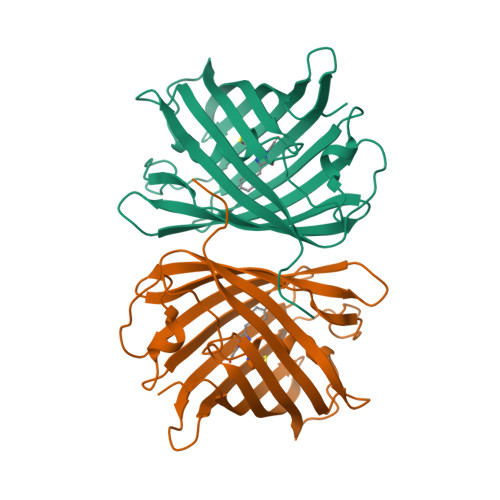
Over the rainbow: structural characterization of the chromoproteins gfasPurple, amilCP, spisPink and eforRed.
Ahmed, F.H., Caputo, A.T., French, N.G., Peat, T.S., Whitfield, J., Warden, A.C., Newman, J., Scott, C.(2022) Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 78: 599-612
- PubMed: 35503208
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798322002625
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7SWR, 7SWS, 7SWT, 7SWU - PubMed Abstract:
Anthozoan chromoproteins are highly pigmented, diversely coloured and readily produced in recombinant expression systems. While they are a versatile and powerful building block in synthetic biology for applications such as biosensor development, they are not widely used in comparison to the related fluorescent proteins, partly due to a lack of structural characterization to aid protein engineering. Here, high-resolution X-ray crystal structures of four open-source chromoproteins, gfasPurple, amilCP, spisPink and eforRed, are presented. These proteins are dimers in solution, and mutation at the conserved dimer interface leads to loss of visible colour development in gfasPurple. The chromophores are trans and noncoplanar in gfasPurple, amilCP and spisPink, while that in eforRed is cis and noncoplanar, and also emits fluorescence. Like other characterized chromoproteins, gfasPurple, amilCP and eforRed contain an sp 2 -hybridized N-acylimine in the peptide bond preceding the chromophore, while spisPink is unusual and demonstrates a true sp 3 -hybridized trans-peptide bond at this position. It was found that point mutations at the chromophore-binding site in gfasPurple that substitute similar amino acids to those in amilCP and spisPink generate similar colours. These features and observations have implications for the utility of these chromoproteins in protein engineering and synthetic biology applications.
Organizational Affiliation:
Land and Water, CSIRO, Clunies Ross Street, Canberra, ACT 2601, Australia.