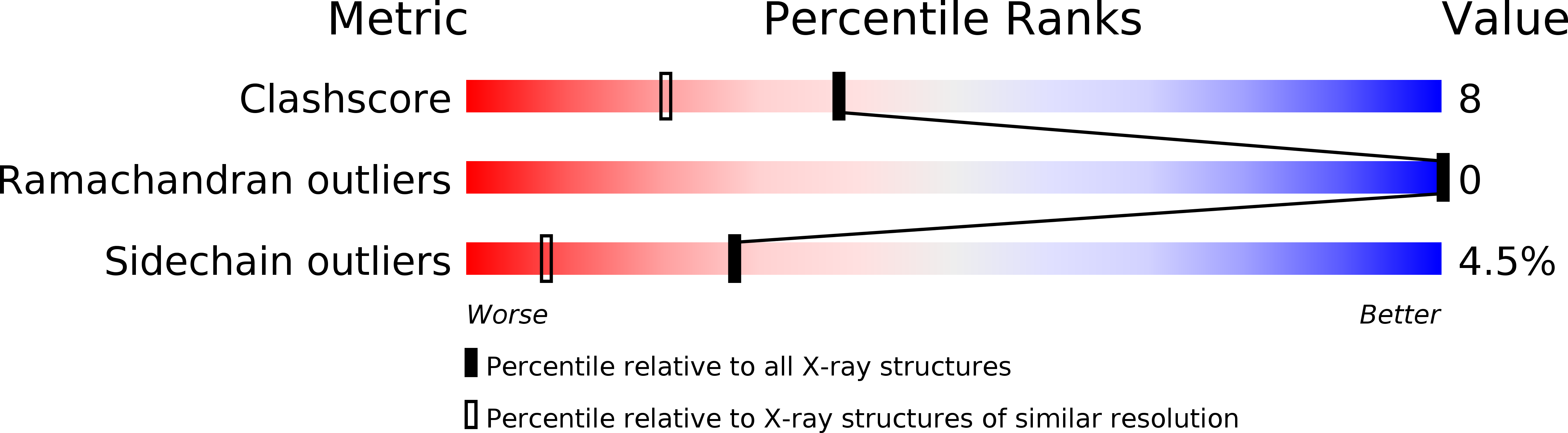Structural effects induced by removal of a disulfide-bridge: the X-ray structure of the C30A/C51A mutant of basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor at 1.6 A.
Eigenbrot, C., Randal, M., Kossiakoff, A.A.(1990) Protein Eng 3: 591-598
- PubMed: 1699222
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/protein/3.7.591
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7PTI - PubMed Abstract:
The X-ray structure of a variant of basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI) has been analyzed to determine the structural accommodation resulting from removal of a disulfide cross-link in a protein. The disulfide removed, Cys30-Cys51, has been implicated in both the folding pathway of the protein and its overall thermal stability. In the variant studied, C30A/C51A, the disulfide cysteines were replaced by less bulky alanines. The atomic displacements observed for C30A/C51A indicate a set of concerted shifts of two segments of chains, which together significantly diminish a packing defect at the site of the removed cysteine sulfur atoms. The observed structural changes are distributed asymmetrically around the sites of mutation, indicating that the adjacent beta-sheet is more resistant to the perturbation than the alpha-helix on the opposite side of the disulfide bond. The thermal parameters of groups involved in the structural accommodation are not significantly altered. A comparison of the X-ray structures reported for native BPTI determined in three different crystal forms indicates that the magnitude of its conformational variability exceeds that of the structural changes caused by the disulfide removal. This emphasizes the necessity of using isomorphous crystal systems to determine the relatively small effects due to mutation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biomolecular Chemistry, Genentech Inc., South San Francisco, CA 94080.