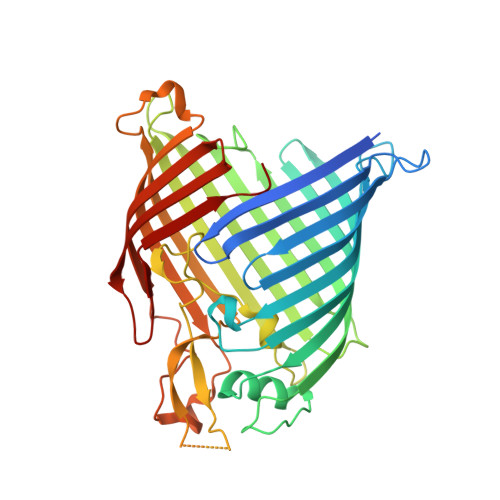
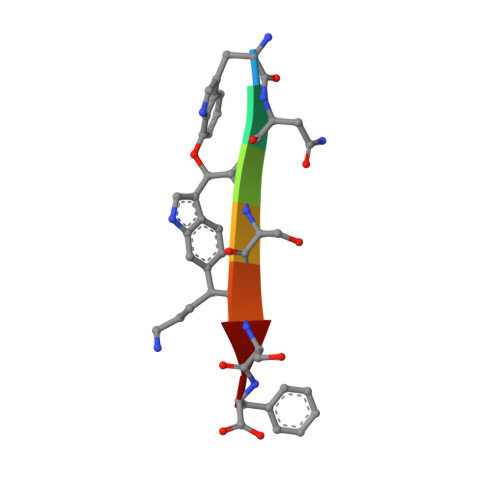
The antibiotic darobactin mimics a beta-strand to inhibit outer membrane insertase.
Kaur, H., Jakob, R.P., Marzinek, J.K., Green, R., Imai, Y., Bolla, J.R., Agustoni, E., Robinson, C.V., Bond, P.J., Lewis, K., Maier, T., Hiller, S.(2021) Nature 593: 125-129
- PubMed: 33854236
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03455-w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7NRE, 7NRF, 7NRI - PubMed Abstract:
Antibiotics that target Gram-negative bacteria in new ways are needed to resolve the antimicrobial resistance crisis 1-3 . Gram-negative bacteria are protected by an additional outer membrane, rendering proteins on the cell surface attractive drug targets 4,5 . The natural compound darobactin targets the bacterial insertase BamA 6 -the central unit of the essential BAM complex, which facilitates the folding and insertion of outer membrane proteins 7-13 . BamA lacks a typical catalytic centre, and it is not obvious how a small molecule such as darobactin might inhibit its function. Here we resolve the mode of action of darobactin at the atomic level using a combination of cryo-electron microscopy, X-ray crystallography, native mass spectrometry, in vivo experiments and molecular dynamics simulations. Two cyclizations pre-organize the darobactin peptide in a rigid β-strand conformation. This creates a mimic of the recognition signal of native substrates with a superior ability to bind to the lateral gate of BamA. Upon binding, darobactin replaces a lipid molecule from the lateral gate to use the membrane environment as an extended binding pocket. Because the interaction between darobactin and BamA is largely mediated by backbone contacts, it is particularly robust against potential resistance mutations. Our results identify the lateral gate as a functional hotspot in BamA and will allow the rational design of antibiotics that target this bacterial Achilles heel.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biozentrum, University of Basel, Basel, Switzerland.