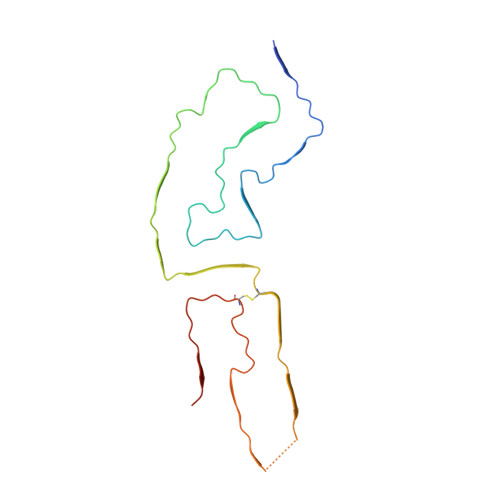
High-resolution structure and strain comparison of infectious mammalian prions.
Kraus, A., Hoyt, F., Schwartz, C.L., Hansen, B., Artikis, E., Hughson, A.G., Raymond, G.J., Race, B., Baron, G.S., Caughey, B.(2021) Mol Cell 81: 4540
- PubMed: 34433091
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2021.08.011
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7LNA - PubMed Abstract:
Within the extensive range of self-propagating pathologic protein aggregates of mammals, prions are the most clearly infectious (e.g., ∼10 9 lethal doses per milligram). The structures of such lethal assemblies of PrP molecules have been poorly understood. Here we report a near-atomic core structure of a brain-derived, fully infectious prion (263K strain). Cryo-electron microscopy showed amyloid fibrils assembled with parallel in-register intermolecular β sheets. Each monomer provides one rung of the ordered fibril core, with N-linked glycans and glycolipid anchors projecting outward. Thus, single monomers form the templating surface for incoming monomers at fibril ends, where prion growth occurs. Comparison to another prion strain (aRML) revealed major differences in fibril morphology but, like 263K, an asymmetric fibril cross-section without paired protofilaments. These findings provide structural insights into prion propagation, strains, species barriers, and membrane pathogenesis. This structure also helps frame considerations of factors influencing the relative transmissibility of other pathologic amyloids.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pathology, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, OH 44106, USA. Electronic address: alk127@case.edu.