Host-emitted amino acid cues regulate bacterial chemokinesis to enhance colonization.
Robinson, C.D., Sweeney, E.G., Ngo, J., Ma, E., Perkins, A., Smith, T.J., Fernandez, N.L., Waters, C.M., Remington, S.J., Bohannan, B.J.M., Guillemin, K.(2021) Cell Host Microbe 29: 1221
- PubMed: 34233153
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2021.06.003
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
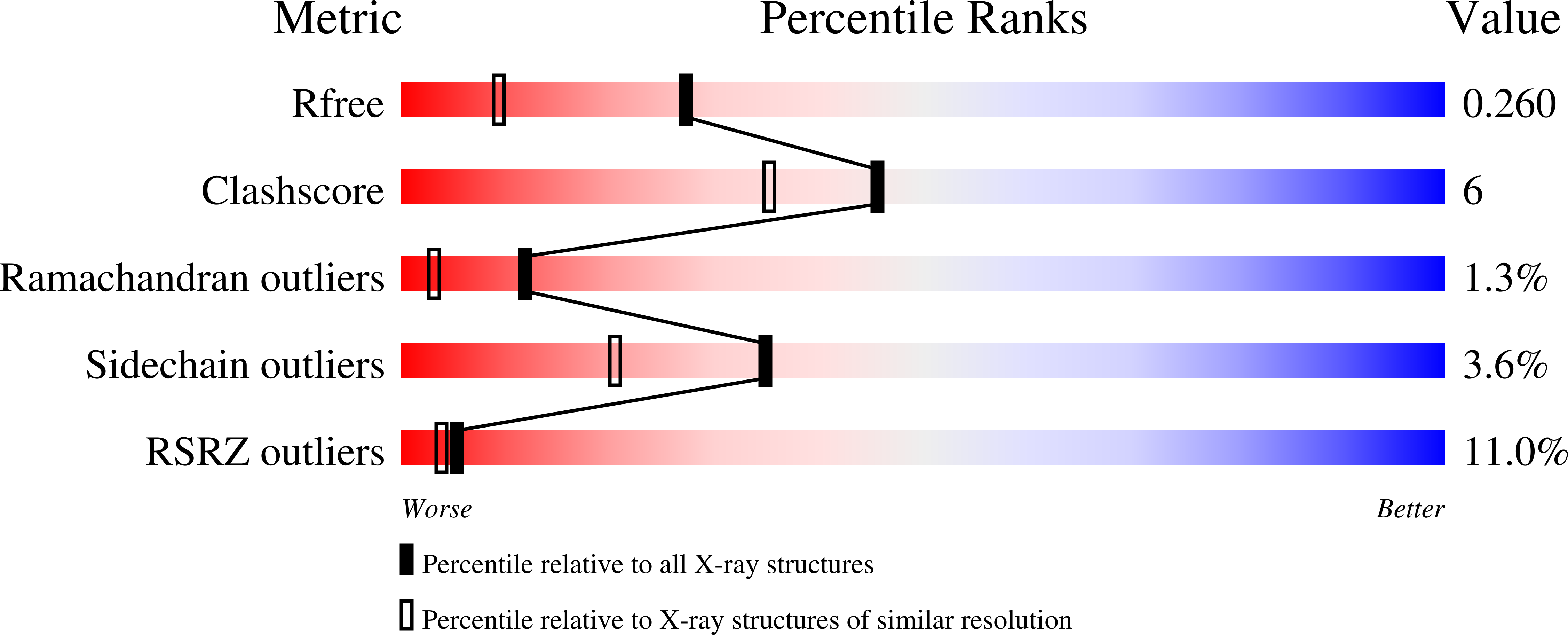
7K5N - PubMed Abstract:
Animal microbiomes are assembled predominantly from environmental microbes, yet the mechanisms by which individual symbionts regulate their transmission into hosts remain underexplored. By tracking the experimental evolution of Aeromonas veronii in gnotobiotic zebrafish, we identify bacterial traits promoting host colonization. Multiple independently evolved isolates with increased immigration harbored mutations in a gene we named sensor of proline diguanylate cyclase enzyme (SpdE) based on structural, biochemical, and phenotypic evidence that SpdE encodes an amino-acid-sensing diguanylate cyclase. SpdE detects free proline and to a lesser extent valine and isoleucine, resulting in reduced production of intracellular c-di-GMP, a second messenger controlling bacterial motility. Indeed, SpdE binding to amino acids increased bacterial motility and host colonization. Hosts serve as sources of SpdE-detected amino acids, with levels varying based on microbial colonization status. Our work demonstrates that bacteria use chemically regulated motility, or chemokinesis, to sense host-emitted cues that trigger active immigration into hosts.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Molecular Biology, University of Oregon, Eugene, OR 97403, USA.