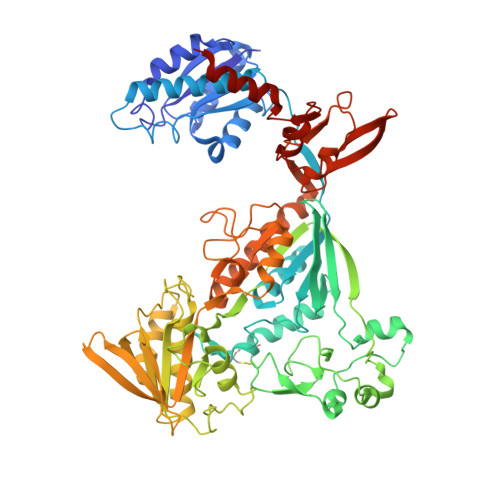
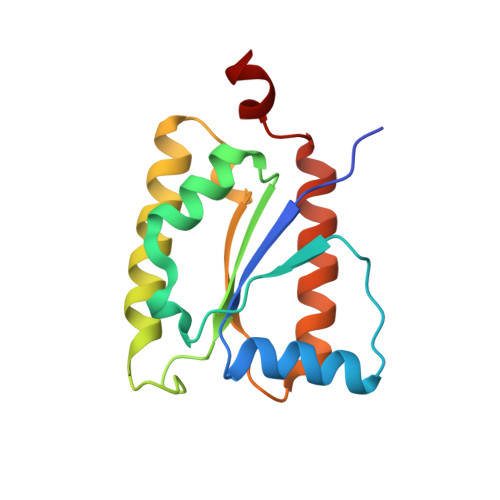
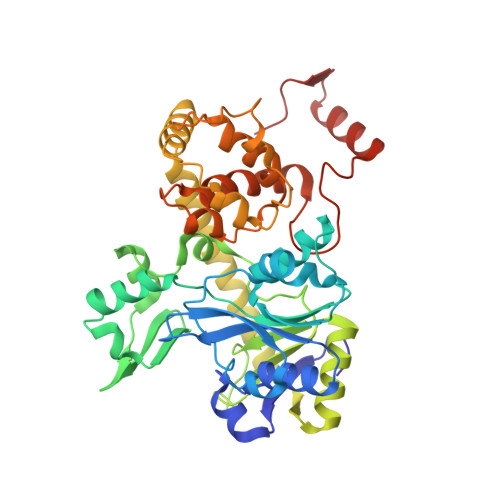
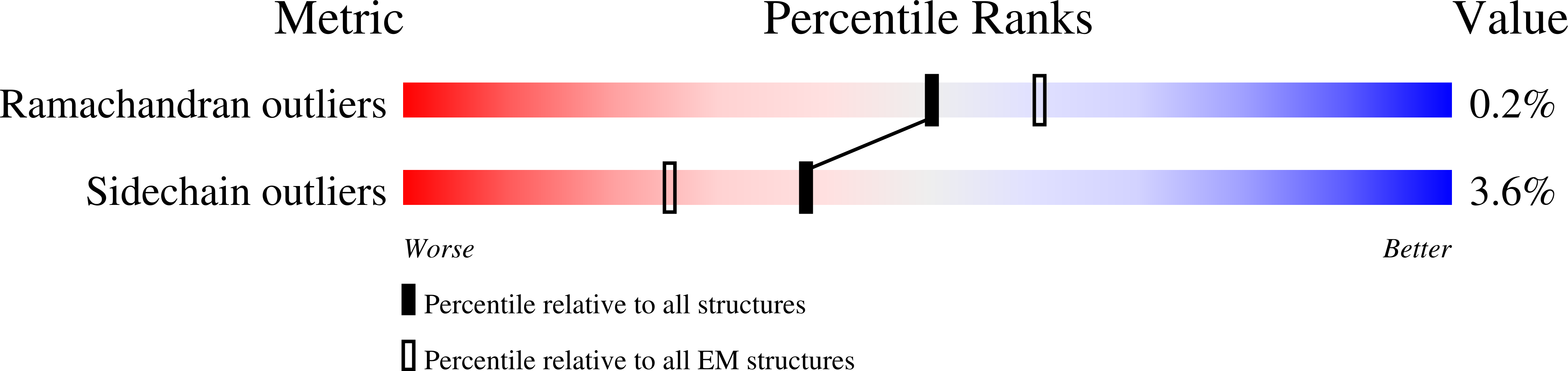Three-megadalton complex of methanogenic electron-bifurcating and CO 2 -fixing enzymes.
Watanabe, T., Pfeil-Gardiner, O., Kahnt, J., Koch, J., Shima, S., Murphy, B.J.(2021) Science 373: 1151-1156
- PubMed: 34516836
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abg5550
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7BKB, 7BKC, 7BKD, 7BKE - PubMed Abstract:
The first reaction of the methanogenic pathway from carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is the reduction and condensation of CO 2 to formyl-methanofuran, catalyzed by formyl-methanofuran dehydrogenase (Fmd). Strongly reducing electrons for this reaction are generated by heterodisulfide reductase (Hdr) in complex with hydrogenase or formate dehydrogenase (Fdh) using a flavin-based electron-bifurcation mechanism. Here, we report enzymological and structural characterizations of Fdh-Hdr-Fmd complexes from Methanospirillum hungatei . The complexes catalyze this reaction using electrons from formate and the reduced form of the electron carrier F 420 . Conformational changes in HdrA mediate electron bifurcation, and polyferredoxin FmdF directly transfers electrons to the CO 2 reduction site, as evidenced by methanofuran-dependent flavin-based electron bifurcation even without free ferredoxin, a diffusible electron carrier between Hdr and Fmd. Conservation of Hdr and Fmd structures suggests that this complex is common among hydrogenotrophic methanogens.
Organizational Affiliation:
Microbial Protein Structure Group, Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology, 35043 Marburg, Germany.