Structural and biological insights into Klebsiella pneumoniae surface polysaccharide degradation by a bacteriophage K1 lyase: implications for clinical use.
Tu, I.F., Lin, T.L., Yang, F.L., Lee, I.M., Tu, W.L., Liao, J.H., Ko, T.P., Wu, W.J., Jan, J.T., Ho, M.R., Chou, C.Y., Wang, A.H., Wu, C.Y., Wang, J.T., Huang, K.F., Wu, S.H.(2022) J Biomed Sci 29: 9-9
- PubMed: 35130876
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-022-00792-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7W1C, 7W1D, 7W1E - PubMed Abstract:
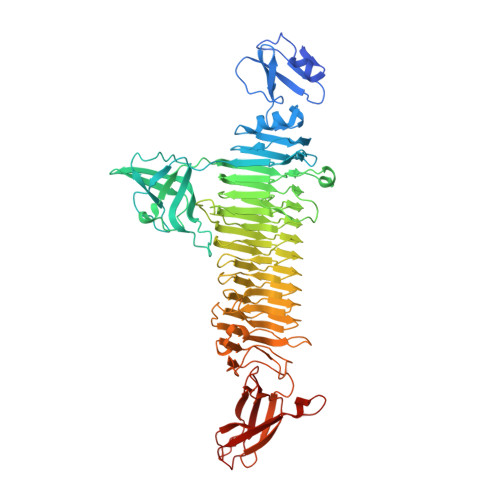
K1 capsular polysaccharide (CPS)-associated Klebsiella pneumoniae is the primary cause of pyogenic liver abscesses (PLA) in Asia. Patients with PLA often have serious complications, ultimately leading to a mortality of ~ 5%. This K1 CPS has been reported as a promising target for development of glycoconjugate vaccines against K. pneumoniae infection. The pyruvylation and O-acetylation modifications on the K1 CPS are essential to the immune response induced by the CPS. To date, however, obtaining the fragments of K1 CPS that contain the pyruvylation and O-acetylation for generating glycoconjugate vaccines still remains a challenge. We analyzed the digested CPS products with NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry to reveal a bacteriophage-derived polysaccharide depolymerase specific to K1 CPS. The biochemical and biophysical properties of the enzyme were characterized and its crystal structures containing bound CPS products were determined. We also performed site-directed mutagenesis, enzyme kinetic analysis, phage absorption and infectivity studies, and treatment of the K. pneumoniae-infected mice with the wild-type and mutant enzymes. We found a bacteriophage-derived polysaccharide lyase that depolymerizes the K1 CPS into fragments of 1-3 repeating trisaccharide units with the retention of the pyruvylation and O-acetylation, and thus the important antigenic determinants of intact K1 CPS. We also determined the 1.46-Å-resolution, product-bound crystal structure of the enzyme, revealing two distinct carbohydrate-binding sites in a trimeric β-helix architecture, which provide the first direct evidence for a second, non-catalytic, carbohydrate-binding site in bacteriophage-derived polysaccharide depolymerases. We demonstrate the tight interaction between the pyruvate moiety of K1 CPS and the enzyme in this second carbohydrate-binding site to be crucial to CPS depolymerization of the enzyme as well as phage absorption and infectivity. We also demonstrate that the enzyme is capable of protecting mice from K1 K. pneumoniae infection, even against a high challenge dose. Our results provide insights into how the enzyme recognizes and depolymerizes the K1 CPS, and demonstrate the potential use of the protein not only as a therapeutic agent against K. pneumoniae, but also as a tool to prepare structurally-defined oligosaccharides for the generation of glycoconjugate vaccines against infections caused by this organism.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biological Chemistry, Academia Sinica, No. 128 Academia Road Section 2, Nan‑Kang, Taipei, 115, Taiwan.