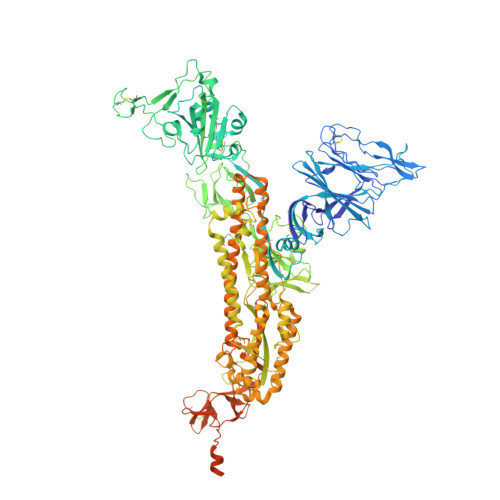
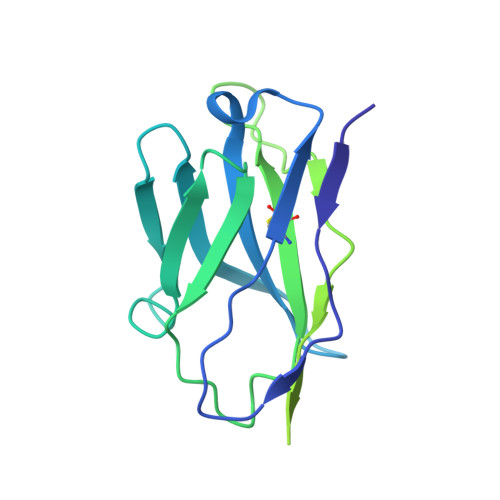
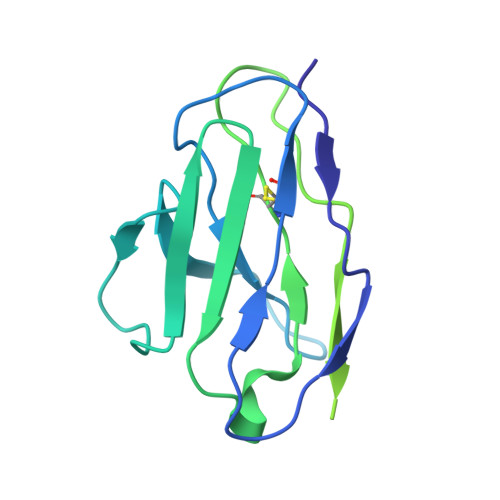
Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies elicited by mosaic RBD nanoparticles bind conserved sarbecovirus epitopes.
Fan, C., Cohen, A.A., Park, M., Hung, A.F., Keeffe, J.R., Gnanapragasam, P.N.P., Lee, Y.E., Gao, H., Kakutani, L.M., Wu, Z., Kleanthous, H., Malecek, K.E., Williams, J.C., Bjorkman, P.J.(2022) Immunity 55: 2419
- PubMed: 36370711
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2022.10.019
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7UZ4, 7UZ5, 7UZ6, 7UZ7, 7UZ8, 7UZ9, 7UZA, 7UZB, 7UZC, 7UZD - PubMed Abstract:
Increased immune evasion by SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern highlights the need for new therapeutic neutralizing antibodies. Immunization with nanoparticles co-displaying spike receptor-binding domains (RBDs) from eight sarbecoviruses (mosaic-8 RBD-nanoparticles) efficiently elicits cross-reactive polyclonal antibodies against conserved sarbecovirus RBD epitopes. Here, we identified monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) capable of cross-reactive binding and neutralization of animal sarbecoviruses and SARS-CoV-2 variants by screening single mouse B cells secreting IgGs that bind two or more sarbecovirus RBDs. Single-particle cryo-EM structures of antibody-spike complexes, including a Fab-Omicron complex, mapped neutralizing mAbs to conserved class 1/4 RBD epitopes. Structural analyses revealed neutralization mechanisms, potentials for intra-spike trimer cross-linking by IgGs, and induced changes in trimer upon Fab binding. In addition, we identified a mAb-resembling Bebtelovimab, an EUA-approved human class 3 anti-RBD mAb. These results support using mosaic RBD-nanoparticle vaccination to generate and identify therapeutic pan-sarbecovirus and pan-variant mAbs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Biology and Biological Engineering, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA.