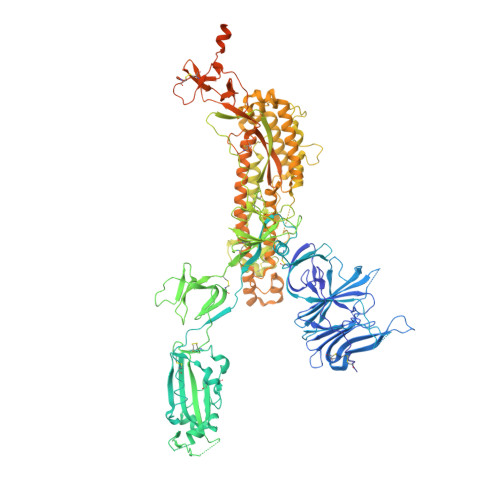
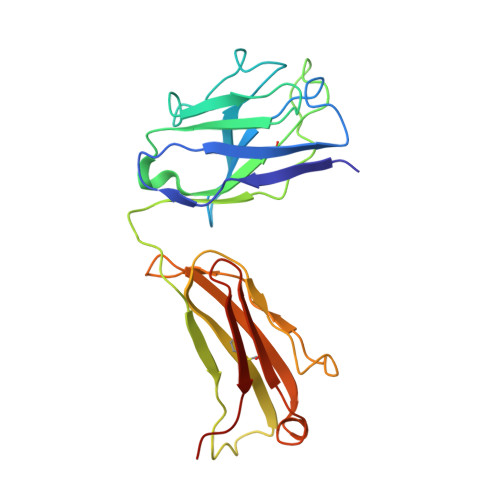
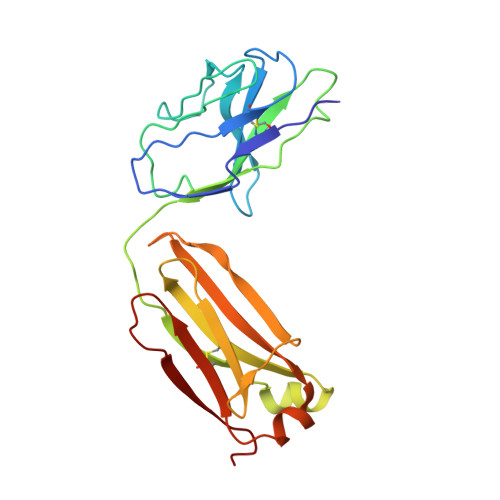
Rapid identification of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants by mRNA display.
Tanaka, S., Olson, C.A., Barnes, C.O., Higashide, W., Gonzalez, M., Taft, J., Richardson, A., Martin-Fernandez, M., Bogunovic, D., Gnanapragasam, P.N.P., Bjorkman, P.J., Spilman, P., Niazi, K., Rabizadeh, S., Soon-Shiong, P.(2022) Cell Rep 38: 110348-110348
- PubMed: 35114110
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110348
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7S0B, 7S0C, 7S0D, 7S0E - PubMed Abstract:
The increasing prevalence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants with the ability to escape existing humoral protection conferred by previous infection and/or immunization necessitates the discovery of broadly reactive neutralizing antibodies (nAbs). Utilizing mRNA display, we identify a set of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) proteins and characterize the structures of nAbs that recognize epitopes in the S1 subunit of the S glycoprotein. These structural studies reveal distinct binding modes for several antibodies, including the targeting of rare cryptic epitopes in the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of S that interact with angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) to initiate infection, as well as the S1 subdomain 1. Further, we engineer a potent ACE2-blocking nAb to sustain binding to S RBD with the E484K and L452R substitutions found in multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants. We demonstrate that mRNA display is an approach for the rapid identification of nAbs that can be used in combination to combat emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Organizational Affiliation:
ImmunityBio, Inc., 9920 Jefferson Boulevard, Culver City, CA 90232, USA.