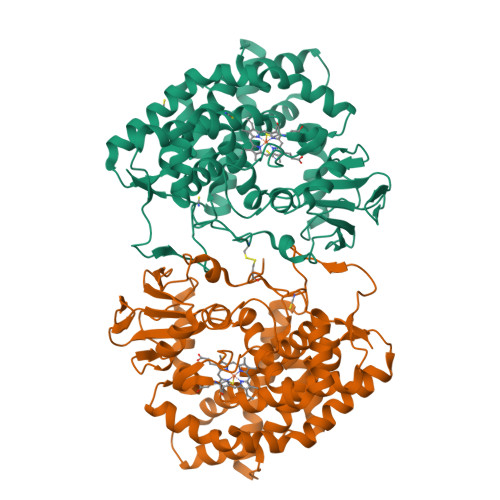
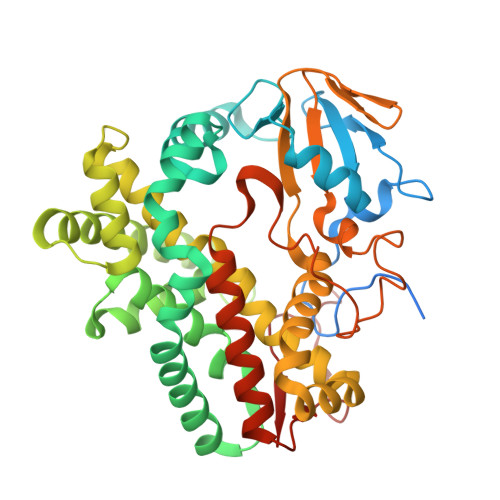
P450-mediated dehydrotyrosine formation during WS9326 biosynthesis proceeds via dehydrogenation of a specific acylated dipeptide substrate.
Zhang, S., Zhang, L., Greule, A., Tailhades, J., Marschall, E., Prasongpholchai, P., Leng, D.J., Zhang, J., Zhu, J., Kaczmarski, J.A., Schittenhelm, R.B., Einsle, O., Jackson, C.J., Alberti, F., Bechthold, A., Zhang, Y., Tosin, M., Si, T., Cryle, M.J.(2023) Acta Pharm Sin B 13: 3561-3574
- PubMed: 37655329
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2023.03.021
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7OQ6 - PubMed Abstract:
WS9326A is a peptide antibiotic containing a highly unusual N -methyl- E -2-3-dehydrotyrosine (NMet-Dht) residue that is incorporated during peptide assembly on a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS). The cytochrome P450 encoded by sas16 (P450 Sas ) has been shown to be essential for the formation of the alkene moiety in NMet-Dht, but the timing and mechanism of the P450 Sas -mediated α , β -dehydrogenation of Dht remained unclear. Here, we show that the substrate of P450 Sas is the NRPS-associated peptidyl carrier protein (PCP)-bound dipeptide intermediate ( Z )-2-pent-1'-enyl-cinnamoyl-Thr- N -Me-Tyr. We demonstrate that P450 Sas -mediated incorporation of the double bond follows N -methylation of the Tyr by the N- methyl transferase domain found within the NRPS, and further that P450 Sas appears to be specific for substrates containing the ( Z )-2-pent-1'-enyl-cinnamoyl group. A crystal structure of P450 Sas reveals differences between P450 Sas and other P450s involved in the modification of NRPS-associated substrates, including the substitution of the canonical active site alcohol residue with a phenylalanine (F250), which in turn is critical to P450 Sas activity and WS9326A biosynthesis. Together, our results suggest that P450 Sas catalyses the direct dehydrogenation of the NRPS-bound dipeptide substrate, thus expanding the repertoire of P450 enzymes that can be used to produce biologically active peptides.
Organizational Affiliation:
CAS Key Laboratory of Quantitative Engineering Biology, Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology, Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen 518055, China.