The 14-3-3/SLP76 protein-protein interaction in T-cell receptor signalling: a structural and biophysical characterization.
Soini, L., Leysen, S., Davis, J., Westwood, M., Ottmann, C.(2021) FEBS Lett 595: 404-414
- PubMed: 33159816
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13993
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6ZCJ - PubMed Abstract:
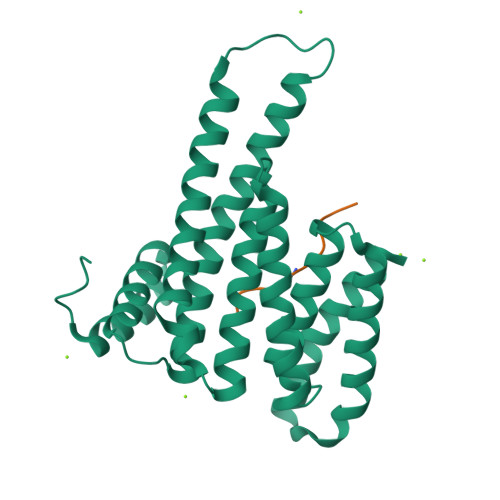
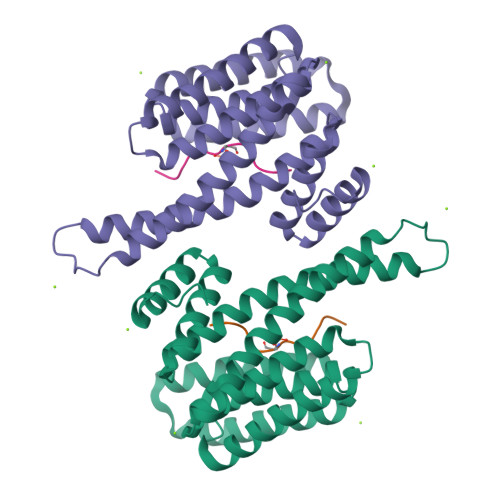
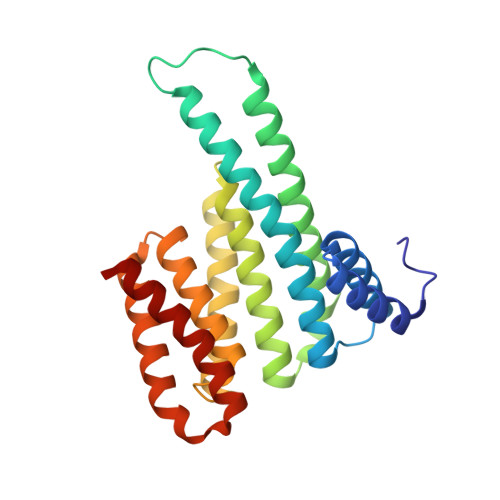
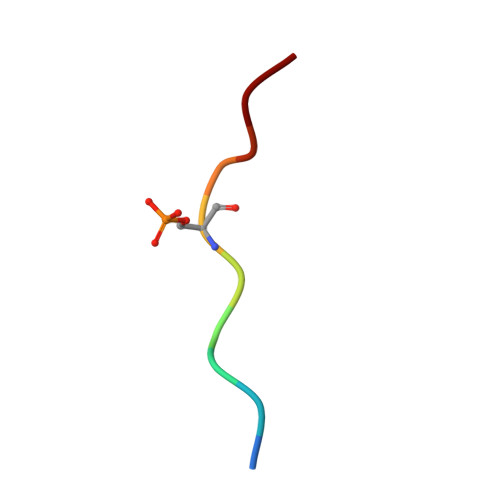
The SH2 domain-containing protein of 76 kDa, SLP76, is an important adaptor protein that coordinates a complex protein network downstream of T-cell receptors (TCR), ultimately regulating the immune response. Upon phosphorylation on Ser376, SLP76 interacts with 14-3-3 adaptor proteins, which leads to its proteolytic degradation. This provides a negative feedback mechanism by which TCR signalling can be controlled. To gain insight into the 14-3-3/SLP76 protein-protein interaction (PPI), we have determined a high-resolution crystal structure of a SLP76 synthetic peptide containing Ser376 with 14-3-3σ. We then characterized its binding to 14-3-3 proteins biophysically by means of fluorescence polarization and isothermal titration calorimetry. Furthermore, we generated two recombinant SLP76 protein constructs and characterized their binding to 14-3-3. Our work lays the foundation for drug design efforts aimed at targeting the 14-3-3/SLP76 interaction and, thereby, TCR signalling.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Chemical Biology, Department of Biomedical Engineering and Institute for Complex Molecular Systems, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, the Netherlands.