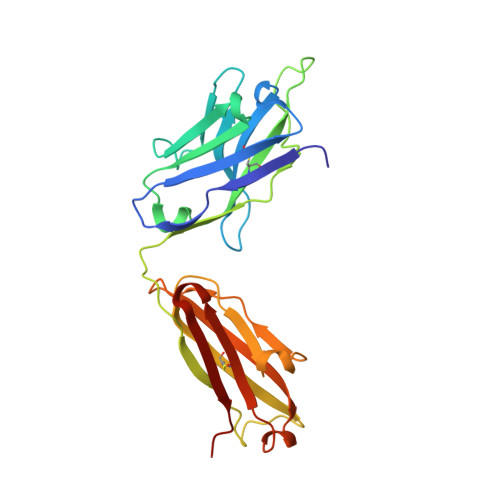
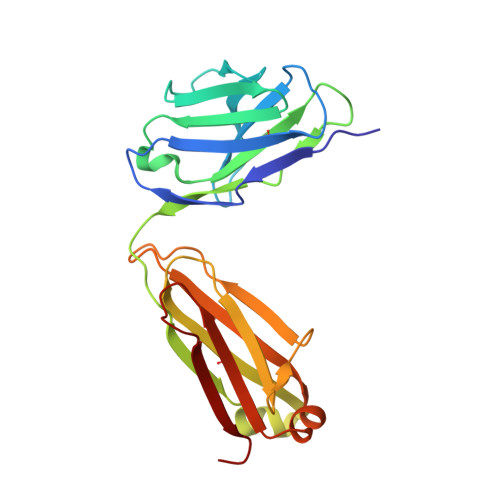
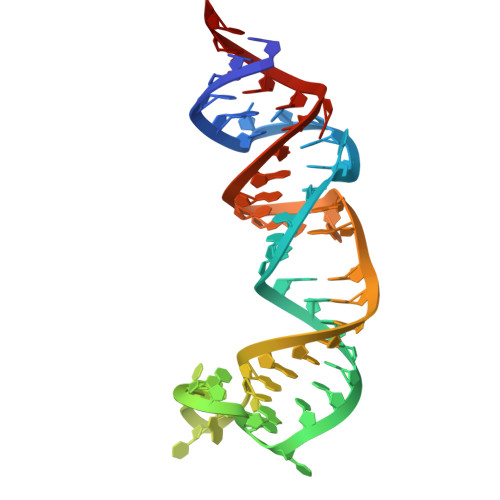
Structural basis for substrate binding and catalysis by a self-alkylating ribozyme.
Krochmal, D., Shao, Y., Li, N.S., DasGupta, S., Shelke, S.A., Koirala, D., Piccirilli, J.A.(2022) Nat Chem Biol 18: 376-384
- PubMed: 35058645
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-021-00950-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6XJQ, 6XJW, 6XJY, 6XJZ - PubMed Abstract:
Ribozymes that react with small-molecule probes have important applications in transcriptomics and chemical biology, such as RNA labeling and imaging. Understanding the structural basis for these RNA-modifying reactions will enable the development of better tools for studying RNA. Nevertheless, high-resolution structures and underlying catalytic mechanisms for members of this ribozyme class remain elusive. Here, we focus on a self-alkylating ribozyme that catalyzes nitrogen-carbon bond formation between a specific guanine and a 2,3-disubstituted epoxide substrate and report the crystal structures of a self-alkylating ribozyme, including both alkylated and apo forms, at 1.71-Å and 2.49-Å resolution, respectively. The ribozyme assumes an elongated hairpin-like architecture preorganized to accommodate the epoxide substrate in a hook-shaped conformation. Observed reactivity of substrate analogs together with an inverse, log-linear pH dependence of the reaction rate suggests a requirement for epoxide protonation, possibly assisted by the ether oxygens within the substrate.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, The University of Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA.