Anin silico-in vitroPipeline Identifying an HLA-A*02:01+KRAS G12V+Spliced Epitope Candidate for a Broad Tumor-Immune Response in Cancer Patients.
Mishto, M., Mansurkhodzhaev, A., Ying, G., Bitra, A., Cordfunke, R.A., Henze, S., Paul, D., Sidney, J., Urlaub, H., Neefjes, J., Sette, A., Zajonc, D.M., Liepe, J.(2019) Front Immunol 10: 2572-2572
- PubMed: 31803176
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02572
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6O4Y, 6O4Z, 6O51, 6O53 - PubMed Abstract:
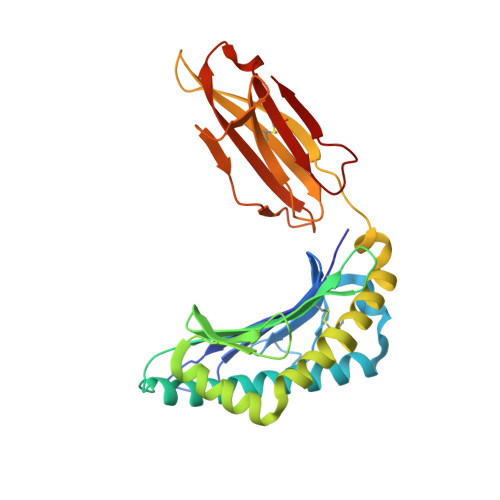
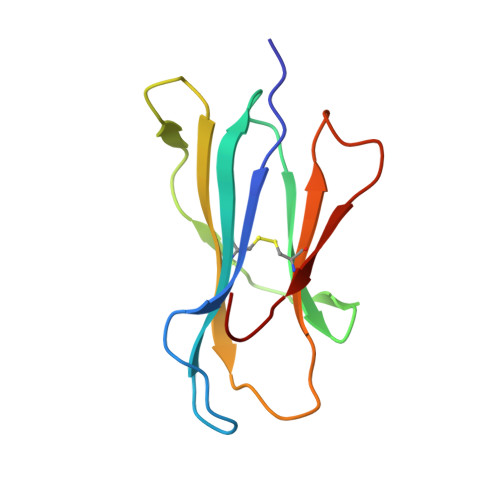
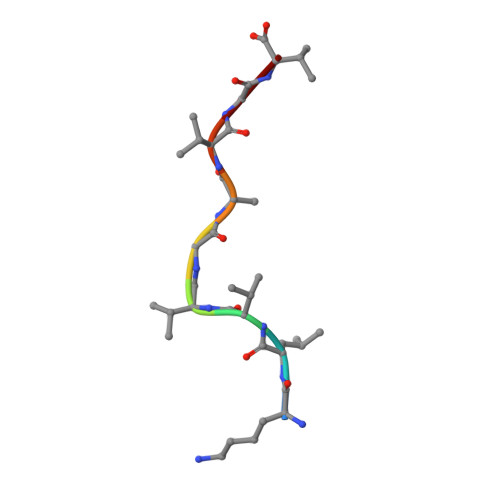
Targeting CD8 + T cells to recurrent tumor-specific mutations can profoundly contribute to cancer treatment. Some of these mutations are potential tumor antigens although they can be displayed by non-spliced epitopes only in a few patients, because of the low affinity of the mutated non-spliced peptides for the predominant HLA class I alleles. Here, we describe a pipeline that uses the large sequence variety of proteasome-generated spliced peptides and identifies spliced epitope candidates, which carry the mutations and bind the predominant HLA-I alleles with high affinity. They could be used in adoptive T cell therapy and other anti-cancer immunotherapies for large cohorts of cancer patients. As a proof of principle, the application of this pipeline led to the identification of a KRAS G12V mutation-carrying spliced epitope candidate, which is produced by proteasomes, transported by TAPs and efficiently presented by the most prevalent HLA class I molecules, HLA-A * 02:01 complexes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centre for Inflammation Biology and Cancer Immunology (CIBCI) & Peter Gorer Department of Immunobiology, King's College London, London, United Kingdom.