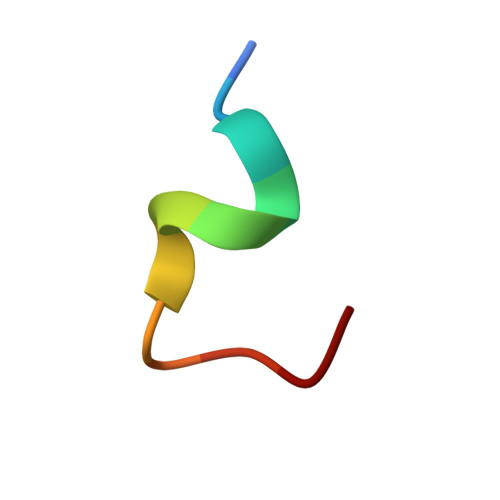
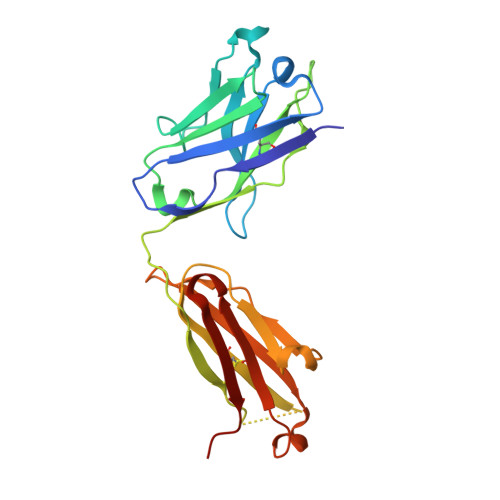
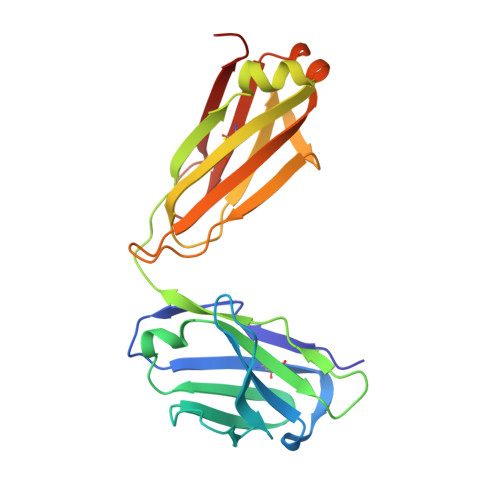
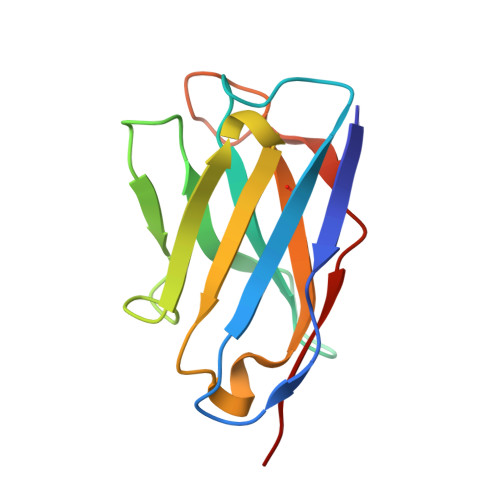
Evolution of protective human antibodies against Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite protein repeat motifs.
Murugan, R., Scally, S.W., Costa, G., Mustafa, G., Thai, E., Decker, T., Bosch, A., Prieto, K., Levashina, E.A., Julien, J.P., Wardemann, H.(2020) Nat Med 26: 1135-1145
- PubMed: 32451496
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0881-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6O23, 6O24, 6O25, 6O26, 6O28, 6O29, 6O2A, 6O2B, 6O2C, 6ULE, 6ULF, 6VLN - PubMed Abstract:
The circumsporozoite protein of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum (PfCSP) is the main target of antibodies that prevent the infection and disease, as shown in animal models. However, the limited efficacy of the PfCSP-based vaccine RTS,S calls for a better understanding of the mechanisms driving the development of the most potent human PfCSP antibodies and identification of their target epitopes. By characterizing 200 human monoclonal PfCSP antibodies induced by sporozoite immunization, we establish that the most potent antibodies bind around a conserved (N/D)PNANPN(V/A) core. High antibody affinity to the core correlates with protection from parasitemia in mice and evolves around the recognition of NANP motifs. The data suggest that the rational design of a next-generation PfCSP vaccine that elicits high-affinity antibody responses against the core epitope will promote the induction of protective humoral immune responses.
Organizational Affiliation:
B Cell Immunology, German Cancer Research Institute (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany.