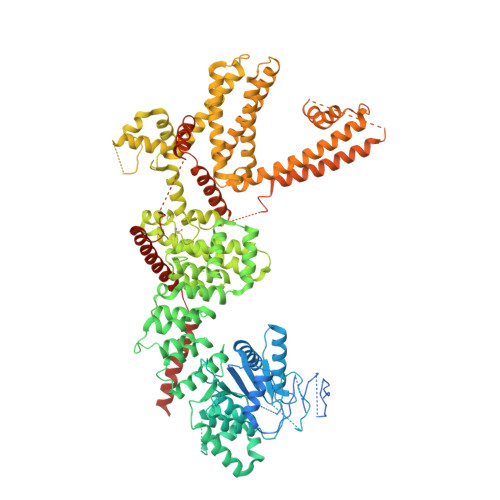
Structural basis of cooling agent and lipid sensing by the cold-activated TRPM8 channel.
Yin, Y., Le, S.C., Hsu, A.L., Borgnia, M.J., Yang, H., Lee, S.Y.(2019) Science 363
- PubMed: 30733385
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aav9334
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6NR2, 6NR3, 6NR4 - PubMed Abstract:
Transient receptor potential melastatin member 8 (TRPM8) is a calcium ion (Ca 2+ )-permeable cation channel that serves as the primary cold and menthol sensor in humans. Activation of TRPM8 by cooling compounds relies on allosteric actions of agonist and membrane lipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP 2 ), but lack of structural information has thus far precluded a mechanistic understanding of ligand and lipid sensing by TRPM8. Using cryo-electron microscopy, we determined the structures of TRPM8 in complex with the synthetic cooling compound icilin, PIP 2 , and Ca 2+ , as well as in complex with the menthol analog WS-12 and PIP 2 Our structures reveal the binding sites for cooling agonists and PIP 2 in TRPM8. Notably, PIP 2 binds to TRPM8 in two different modes, which illustrate the mechanism of allosteric coupling between PIP 2 and agonists. This study provides a platform for understanding the molecular mechanism of TRPM8 activation by cooling agents.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, NC, 27710, USA.