Analysis of insulin glulisine at the molecular level by X-ray crystallography and biophysical techniques.
Gillis, R.B., Solomon, H.V., Govada, L., Oldham, N.J., Dinu, V., Jiwani, S.I., Gyasi-Antwi, P., Coffey, F., Meal, A., Morgan, P.S., Harding, S.E., Helliwell, J.R., Chayen, N.E., Adams, G.G.(2021) Sci Rep 11: 1737-1737
- PubMed: 33462295
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-81251-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6GV0 - PubMed Abstract:
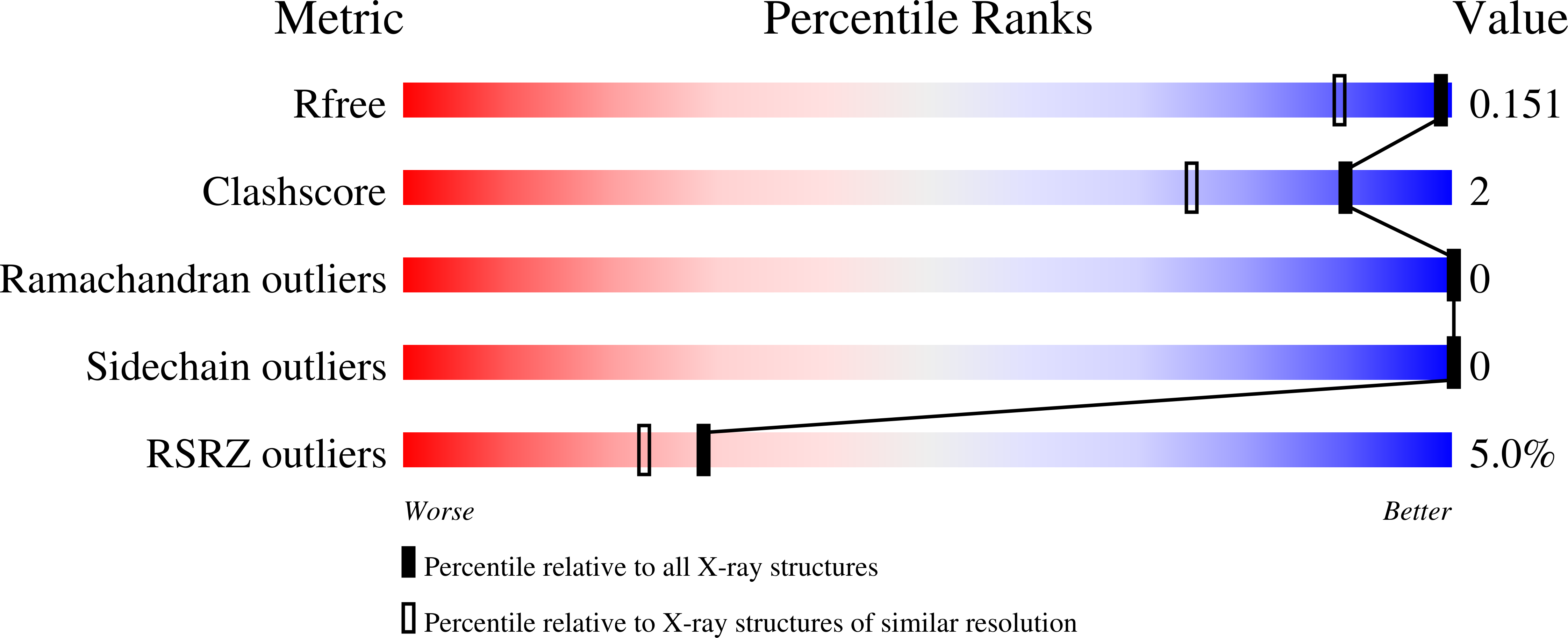
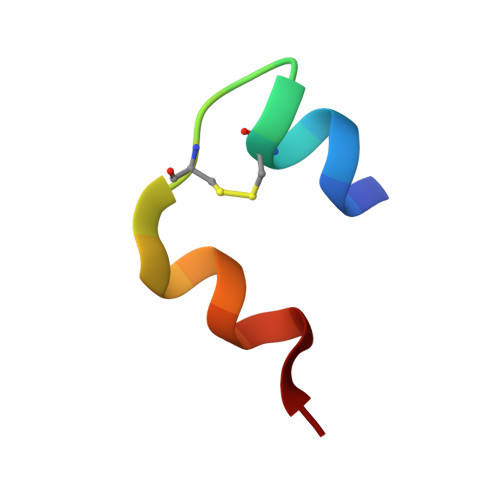
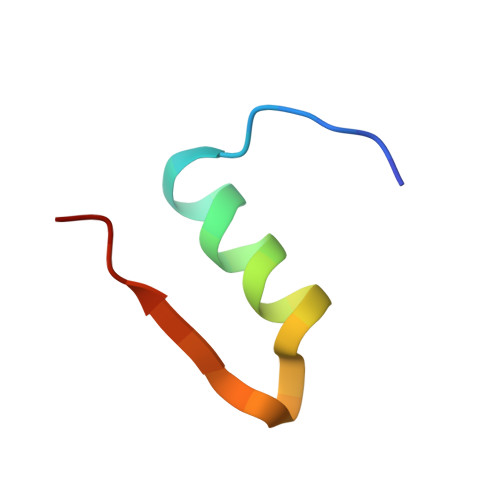
This study concerns glulisine, a rapid-acting insulin analogue that plays a fundamental role in diabetes management. We have applied a combination of methods namely X-ray crystallography, and biophysical characterisation to provide a detailed insight into the structure and function of glulisine. X-ray data provided structural information to a resolution of 1.26 Å. Crystals belonged to the H3 space group with hexagonal (centred trigonal) cell dimensions a = b = 82.44 and c = 33.65 Å with two molecules in the asymmetric unit. A unique position of D21Glu, not present in other fast-acting analogues, pointing inwards rather than to the outside surface was observed. This reduces interactions with neighbouring molecules thereby increasing preference of the dimer form. Sedimentation velocity/equilibrium studies revealed a trinary system of dimers and hexamers/dihexamers in dynamic equilibrium. This new information may lead to better understanding of the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic behaviour of glulisine which might aid in improving formulation regarding its fast-acting role and reducing side effects of this drug.
Organizational Affiliation:
Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Queen's Medical Centre, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, NG7 2HA, UK. richard.gillis@nottingham.ac.uk.