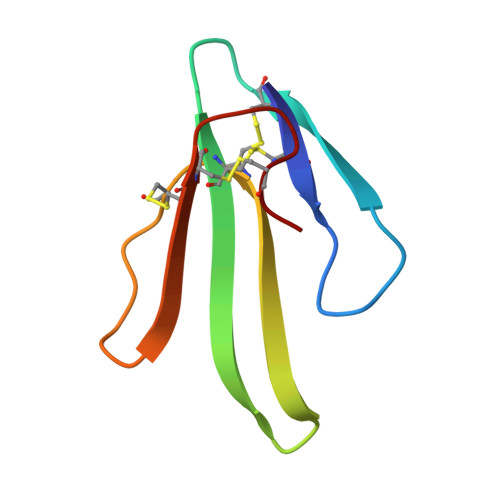
Structure determination of a dimeric form of erabutoxin-b, crystallized from a thiocyanate solution.
Saludjian, P., Prange, T., Navaza, J., Menez, R., Guilloteau, J.P., Ries-Kautt, M., Ducruix, A.(1992) Acta Crystallogr B 48: 520-531
- PubMed: 1418823
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/s010876819200096x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6EBX - PubMed Abstract:
Erabutoxin-b, M(r) = 6861.1, a single 62 amino-acid chain folded by four disulfide bridges, was crystallized in a new orthorhombic form by using thiocyanate as crystallizing agent. The space group is P2(1)2(1)2(1) with a = 53.36 (4), b = 40.89 (4), c = 55.71 (5) A, V = 121533.1 A and Z = 8. X-ray diffraction data were recorded at the LURE synchrotron facility (lambda = 1.405 A). The structure was solved by molecular replacement and shows a dimeric association through an anti-parallel beta-sheet around the twofold non-crystallographic axis. The two independent molecules, one SCN- ion and 97 associated water molecules were refined by molecular dynamics and annealing techniques to R = 19.6% (10,913 Fobs, resolution 5-1.7 A). The thiocyanate ion is located at the interface of the dimer and close to the non-crystallographic twofold axis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Chimie Structurale Bio-moléculaire (URA 1430 CNRS), UFR Biomédicale, Bobigny, France.