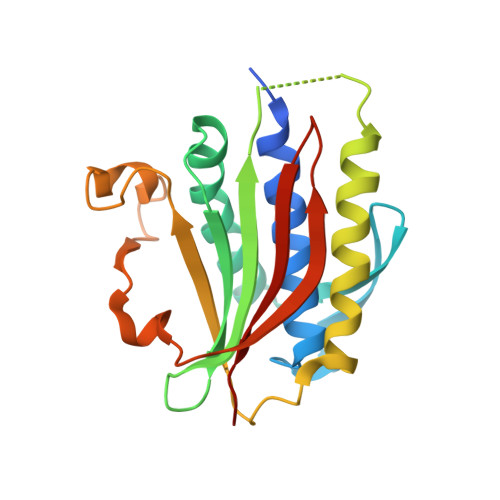
Molecular mechanisms of assembly and TRIP13-mediated remodeling of the human Shieldin complex.
Xie, W., Wang, S., Wang, J., de la Cruz, M.J., Xu, G., Scaltriti, M., Patel, D.J.(2021) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118
- PubMed: 33597306
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2024512118
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6WW9, 6WWA, 7L9P - PubMed Abstract:
The Shieldin complex, composed of REV7, SHLD1, SHLD2, and SHLD3, protects DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) to promote nonhomologous end joining. The AAA + ATPase TRIP13 remodels Shieldin to regulate DNA repair pathway choice. Here we report crystal structures of human SHLD3-REV7 binary and fused SHLD2-SHLD3-REV7 ternary complexes, revealing that assembly of Shieldin requires fused SHLD2-SHLD3 induced conformational heterodimerization of open (O-REV7) and closed (C-REV7) forms of REV7. We also report the cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of the ATPγS-bound fused SHLD2-SHLD3-REV7-TRIP13 complexes, uncovering the principles underlying the TRIP13-mediated disassembly mechanism of the Shieldin complex. We demonstrate that the N terminus of REV7 inserts into the central channel of TRIP13, setting the stage for pulling the unfolded N-terminal peptide of C-REV7 through the central TRIP13 hexameric channel. The primary interface involves contacts between the safety-belt segment of C-REV7 and a conserved and negatively charged loop of TRIP13. This process is mediated by ATP hydrolysis-triggered rotatory motions of the TRIP13 ATPase, thereby resulting in the disassembly of the Shieldin complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Program, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10065; xiew@mskcc.org pateld@mskcc.org.