Convergent structural features of respiratory syncytial virus neutralizing antibodies and plasticity of the site V epitope on prefusion F.
Harshbarger, W., Tian, S., Wahome, N., Balsaraf, A., Bhattacharya, D., Jiang, D., Pandey, R., Tungare, K., Friedrich, K., Mehzabeen, N., Biancucci, M., Chinchilla-Olszar, D., Mallett, C.P., Huang, Y., Wang, Z., Bottomley, M.J., Malito, E., Chandramouli, S.(2020) PLoS Pathog 16: e1008943-e1008943
- PubMed: 33137810
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1008943
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6W52, 6W5D - PubMed Abstract:
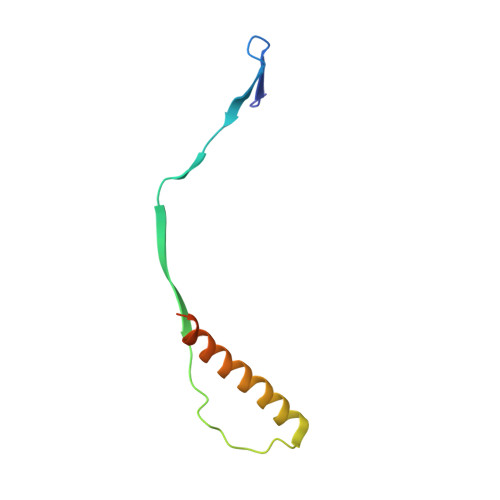
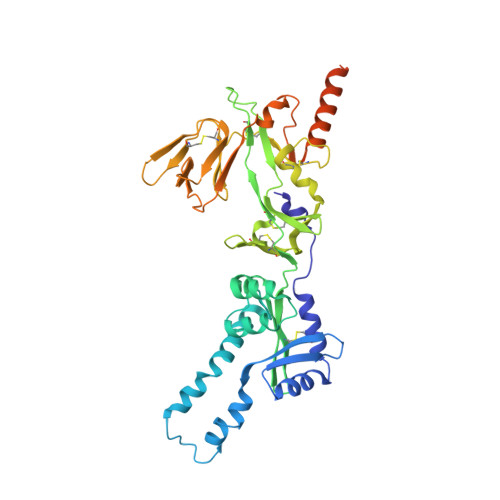
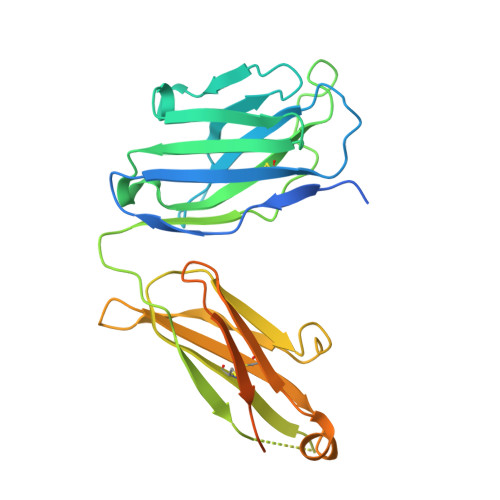
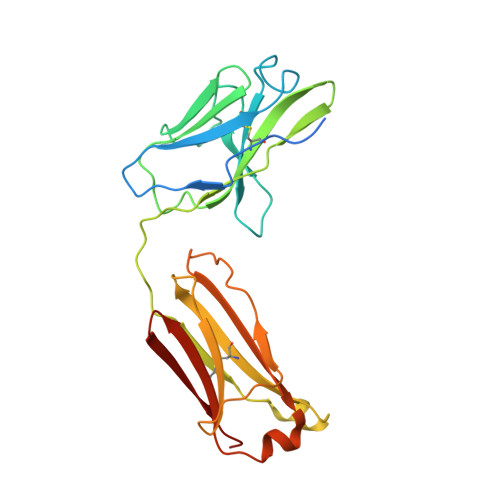
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a global public health burden for which no licensed vaccine exists. To aid vaccine development via increased understanding of the protective antibody response to RSV prefusion glycoprotein F (PreF), we performed structural and functional studies using the human neutralizing antibody (nAb) RSB1. The crystal structure of PreF complexed with RSB1 reveals a conformational, pre-fusion specific site V epitope with a unique cross-protomer binding mechanism. We identify shared structural features between nAbs RSB1 and CR9501, elucidating for the first time how diverse germlines obtained from different subjects can develop convergent molecular mechanisms for recognition of the same PreF site of vulnerability. Importantly, RSB1-like nAbs were induced upon immunization with PreF in naturally-primed cattle. Together, this work reveals new details underlying the immunogenicity of site V and further supports PreF-based vaccine development efforts.
Organizational Affiliation:
GSK, Rockville, MD, United States of America.